
This assumes you know what a thread is. If not, check out this article.
As the name implies, the maintenance thread is a thread that, well, does maintenance. Let's use an example. Let's say you've setup a JDBC data source in WebSphere, so that you can query data from a SQL database.
Now, we don't want the database queries remaining active for a long time, as this would unnecessarily chew up resources (CPU/memory). This is where the maintenance thread comes into play. Every so often, the maintenance thread will check to see if any queries have been idling for a long time. If a database query has been active for too long, the maintenance thread will destroy the query, so as to reclaim resources (that's CPU and memory again).
So, how often does the maintenance thread check for idling connections? It's up to you. In the left panel of the web console, at Resources > JDBC > Data sources > your data source > Connection pool properties, Reap time is the number of seconds between each maintenance thread. By default, reap time is 180 seconds (3 minutes), which means that the maintenance thread will occur once every 3 minutes.
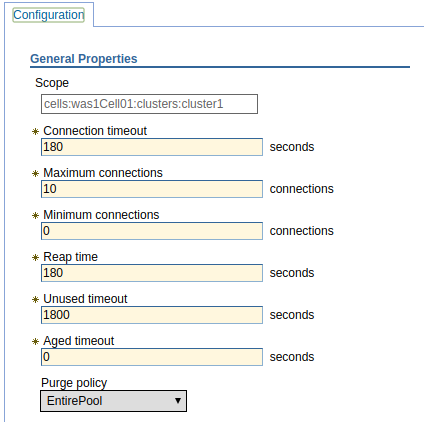
The maintenance thread will destroy connections to the database that have been inactive longer than the unused and/or aged timeout. For example, if the unused timeout is 1800 seconds, and a connection has been inactive longer than 1800 seconds, the maintenance thread will discard the connection until the minimum connections are reached. Similarly, if the aged timeout is 2000 seconds, connections that have been inactive longer than 2000 seconds will be discarded, regardless of the minumum connections value. Reap time can be disabled by setting the value to 0. You usually do not want to decrease the reap time value, as this will decrease the time between maintenance threads, which will put more traffic on the network.
Unused timeout will discard a connection when the current number of connections exceeds the minimum connection setting. In other words, if minimum connections is 10, and there are 5 current connections, the maintenance thread will not destroy the connections to the database when the unused timeout has been exceeded.
Aged timeout will discard a connection that exceeds the aged timeout, regardless of the minimum connections setting. One thing to take into consideration is that there may be other security devices in the network, such as a firewall, that will timeout stale connections. The aged timeout should be less than the firewall timeout, to ensure the firewall never detects an idle connection.
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 