
http response code 404 means that a web server is able to communicate with the client, but the resource being requested by the client cannot be located on the web server. For example, let's say a client requests bogus.html from a web server. If the web server does not contain a file named bogus.html, the web server will respond with http status code 404 not found.
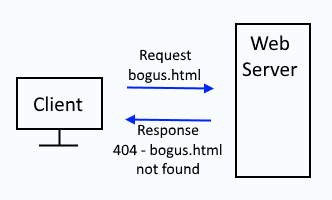
By default, nearly all web servers are configured to display 404 in the browser.
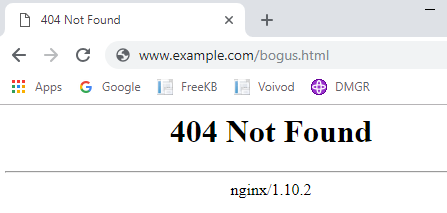
Or, you can check for 404 in the web servers access log.
2018-09-26 01:38:02 10.1.2.3 www.example.com GET "/bogus.html" HTTP/1.1 404
DocumentRoot directive
The DocumentRoot directive in the web servers configuration file must point to the root directory that contains the files that the web server will send to the client, such as HTML and JPG files.
DocumentRoot "/var/www/html"
File ownership and permissions
Let's say 404 Not Found is being returned when requesting index.html. Ensure index.hml exists in the DocumentRoot directory, and that index.html has the appropriate ownership and permissions.
~]# ls -l /var/www/html/index.html
-rw-rw-r-- 1 nobody nobody 185 Nov 19 2013 index.html
Modules
Use the httpd command to ensure all of the web servers modules are properly loaded.
<web_server_root>/bin/httpd -d <web_server_root> -f conf/httpd.conf -M
SELinux
Use the sestatus command to determine if SELinux is enforcing.
Current mode: enforcing
If SELinux is enforcing, one option is to use the setenforce command to temporarily set SELinux to permissive. Or, change the SELinux context of the files on the web server.
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 