
This assumes you have installed HAProxy and HAProxy is configured to load balance requests across two or more PHP servers.
Let's say you have two PHP web servers, www1.example.com and www2.example.com, and these web servers both serve the www.example.com web pages. By default, HAProxy will use round robin to alternate the requests between www1.example.com and www2.example.com. Sticky Sessions can be used so that if a users first request hits www1.example.com, their subsequent requests will go to www1.example.com.
Listen Block
One option would be to use the listen block.
- The prefer-last-server and cookie directives are used for sticky sessions. By default, the name of the PHP Session cookie is PHPSESSID, so as long as you are not using a custom name for the PHP Session cookie, you will use PHPSESSID.
- The httplog, http-request and log-format directives are not needed for sticky sessions, but are really helpful for debugging. Refer to HAProxy Logging for more details on logging.
listen web
bind *:80
mode tcp
balance roundrobin
option httplog
http-request capture req.hdrs len 1024
log-format "%ci:%cp [%tr] %ft [[%hr]] %hs %{+Q}r"
option prefer-last-server
cookie PHPSESSID prefix nocache
server www1 www1.example.com:80 check cookie www1
server www2 www2.example.com:80 check cookie www2
If you have a firewall, such as iptables or firewalld, you will need to allow the HAProxy bind port, not the ports being used by the "server" directives. In this example, only the http (port 80) service would need to be allowed.
firewall-cmd --add-service=http --permanent
firewall-cmd --add-service=https --permanent
firewall-cmd --reload
SInce the httplog, http-request and log-format directives were included, the /var/log/haproxy.log should now show that the header contains the cookie (default-cookie in this example), something like this.
- Notice in this example that the PHPSESSID cookie contains "www1". The prefix option is what includes the server (www1 in this example).
Feb 21 03:27:58 localhost haproxy[6083]: 192.168.0.104:59642 [21/Feb/2022:03:27:58.090] main
[
[
{
host: www.freekb.net
cache-control: max-age=0
upgrade-insecure-requests: 1
user-agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/98.0.4758.102 Safari/537.36
accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.9
referer: http://www.freekb.net/Article?id=12345
accept-encoding: gzip, deflate
accept-language: en-US,en;q=0.9
cookie: PHPSESSID=www1~deuvmrafg6pflii4bus15u4jl9
}
]
]
Frontend / Backend
Or, the frontend and backend blocks can be used. However, this is more commonly used for more complex situations, such as when there are two web servers serving multiple domains.
hdr is short for HTTP headers. For example, the curl command can be used to see the "host" header.
~]$ curl http://www.freekb.net --verbose
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> Host: www.freekb.net
> User-Agent: curl/7.79.1
> Accept: */*
In this example, acl www hdr(host) -i <HTTP header host> is used to route requests to different backends based on the HTTP host header. The -i flag means case insensitive.
frontend main
bind *:80
bind *:443 ssl crt /etc/pki/tls/foo.pem
balance roundrobin
option prefer-last-server
acl www hdr(host) -i www.example.com
use_backend www_example_com if www
default_backend www_example_com
backend www_example_com
cookie PHPSESSID prefix nocache
server www1 www1.example.com:80 check cookie www1
server www2 www2.example.com:80 check cookie www2
Let's say index.php on the www1.example.com web server contains "web server A" and index.php on the other web server www2.example.com contains "web server B". When navigating to http://<HAProxy ip address or hostname>/index.html, lets say the request is routed to www1.example.com (web server A).
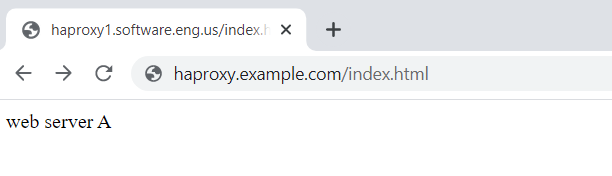
Refreshing the web browser, the subsequent requests should go to www1.example.com (web server A).

Let's consider a slightly different scenario, where the servers www1.example.com and www2.example.com are producing the www.example.com and stage.example.com domains.

If a user's session on www.example.com should be valid for stage.example.com, and vice versa, the important thing to be done is to ensure that the cookie for www1.example.com is the same for each backend (s1 in this example) and the cookie for www2.example.com is the same for each backend (s2 in this example). In this way, if the user hits www1.example.com for the www.example.com domain, then the user will remain on www1.example.com for both the www.example.com and stage.example.com domains.
frontend main
bind *:80
bind *:443 ssl crt /etc/pki/tls/foo.pem
balance roundrobin
option prefer-last-server
acl www hdr(host) -i www.example.com
use_backend www_example_com if www
acl stage hdr(host) -i stage.example.com
use_backend stage_example_com if stage
default_backend www_example_com
backend www_example_com
cookie PHPSESSID prefix nocache
server www1 www1.example.com:80 check cookie s1
server www2 www2.example.com:80 check cookie s2
cookie PHPSESSID prefix nocache
server stage1 www1.example.com:80 check cookie s1
server stage2 www2.example.com:80 check cookie s2
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 