
If you are not familiar with AWS Application Load Balancers, check out my article FreeKB - Amazon Web Services (AWS) - Getting Started with Application Load Balancer (ALB).
Let's say you have two or more EC2 instances that are producing web apps. An application load balancer can be used to load balance the requests for the web app.
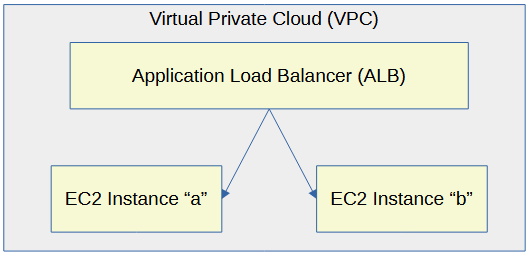
There are a few different types of load balancers.
- Application Load Balancers
- Typically used to load balance requests to a web app
- Typically uses the HTTP and HTTPS protocols
- Cannot be bound to an Elastic IP address (static IP address)
- Network Load Balancers
- Typically used to load balance requests to a SQL database or onto an Application Load Balancer
- Typically uses the TCP protocol
- Can be bound to an Elastic IP address (static IP address)
- Gateway Load Balancers
- Classic Load Balancers (deprecated)
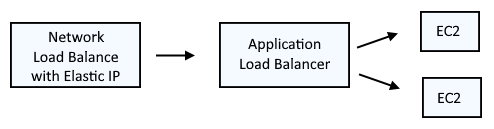
It's important to recognize that an Elastic IP address cannot be assigned to an Application Load Balancer. A common approach is to have a Network Load Balancer with an assigned Elastic IP forward requests onto an Application Load Balancer.
This assumes you have setup Terraform with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) provider. If not, check out my article Amazon Web Services (AWS) Getting Started with Terraform.
Let's say you have the following files on your Terraform server.
├── required_providers.tf
├── application_load_balancers (directory)
│ ├── ec2_instances.tf
│ ├── provider.tf
│ ├── load_balancer.tf
│ ├── security_groups.tf
required_providers.tf will almost always have this.
terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
}
}
}
Let's say provider.tf has the following. In this example, the "default" profile in /home/username/.aws/config and /home/username/.aws/credentials is being used. This assumes you have setup Terraform as described in Amazon Web Services (AWS) - Getting Started with Terraform.
provider "aws" {
alias = "default"
profile = "default"
region = "default"
}
You will be setting up the Application Load Balancer to forward requests onto targets (typically EC2 instances) thus the subnets being used by the Application Load Balancer and Targets (EC2 instances) will need to be in the same Availability Zone. Let's say ec2_instances.tf contains something like this.
data "aws_instance" "docker1" {
filter {
name = "tag:Name"
values = ["docker1"]
}
}
data "aws_instance" "docker2" {
filter {
name = "tag:Name"
values = ["docker2"]
}
}
And let's say security_groups.tf contain the following, to allow traffic into the Application Load Balancer on port 443.
resource "aws_security_group" "alb_security_group" {
name = "application load balancer security group"
description = "application load balancer security group"
vpc_id = data.aws_vpc.default_vpc.id
ingress {
description = "Allow incoming (ingress) requests on port 443"
from_port = 443
to_port = 443
protocol = "TCP"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
tags = {
Name = "application load balancer security group"
}
}
And load_balancer.tf could have the following to create an Application Load Balancer.
resource "aws_lb" "my-application-load-balancer" {
depends_on = [
aws_security_group.alb_security_group,
data.aws_instance.docker1,
data.aws_instance.docker2,
]
name = "my-application-load-balancer"
internal = false
load_balancer_type = "application"
security_groups = [aws_security_group.alb_security_group.id]]
subnets = [data.aws_instance.docker1.subnet_id,data.aws_instance.docker2.subnet_id]
enable_deletion_protection = true
access_logs {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.lb_logs.id
prefix = "my-application-load-balancer"
enabled = true
}
tags = {
Name = "my-application-load-balancer"
}
}
The terraform plan command can be used to see what Terraform will try to do.
terraform plan
And the terraform apply command can be used to create the Elastic Load balancer.
terraform apply
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 