
Let's say you have the following files on your Terraform server.
├── required_providers.tf
├── elastic_container_services (directory)
│ ├── clusters (directory)
│ ├── ├── provider.tf
│ ├── ├── cluster.tf
required_providers.tf will almost always have this.
terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
}
}
}
Let's say provider.tf has the following. In this example, the "default" profile in /home/username/.aws/config and /home/username/.aws/credentials is being used. This assumes you have setup Terraform as described in Amazon Web Services (AWS) - Getting Started with Terraform.
provider "aws" {
alias = "default"
profile = "default"
region = "default"
}
And cluster.tf could have something like this.
resource "aws_ecs_cluster" "my-ecs-cluster" {
name = "my-ecs-cluster"
}
Or like this, to enable Container Insights for Cloudwatch monitoring (such as CPU and Memory usage, et cetera).
resource "aws_ecs_cluster" "my-ecs-cluster" {
name = "my-ecs-cluster"
setting {
name = "containerInsights"
value = "enabled"
}
}
You may need to reissue the terraform init command.
~]# terraform init
Initializing the backend...
Initializing modules...
Initializing provider plugins...
Terraform has been successfully initialized!
The terraform plan command can be used to see what Terraform will try to do.
~]$ terraform plan
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# aws_ecs_cluster.my-ecs-cluster will be created
+ resource "aws_ecs_cluster" "my-ecs-cluster" {
+ arn = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ name = "my-ecs-cluster"
+ tags_all = (known after apply)
+ setting {
+ name = (known after apply)
+ value = (known after apply)
}
}
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
By default, the terraform.tfstate file should be found in your root module directory (/usr/local/terraform/aws in this example).
- If the resource does not exist and the terraform.tfstate file does not contain the resource, Terraform will create the resource.
- If the resource exists and the terraform.tfstate file contains the resource and a difference is found between the resources.tf file and the terraform.tfstate file, Terraform will update the resource.
- If the resource exists and the terraform.tfstate file contains the resource and the resource is removed from the resources.tf file, Terraform will destroy (delete) the resource.
The terraform apply command can be used to create, update or delete the resource.
]$ terraform apply -auto-approve
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# aws_ecs_cluster.my-ecs-cluster will be created
+ resource "aws_ecs_cluster" "my-ecs-cluster" {
+ arn = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ name = "my-ecs-cluster"
+ tags_all = (known after apply)
+ setting {
+ name = (known after apply)
+ value = (known after apply)
}
}
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
aws_ecs_cluster.my-ecs-cluster: Creating...
aws_ecs_cluster.my-ecs-cluster: Still creating... [10s elapsed]
aws_ecs_cluster.my-ecs-cluster: Creation complete after 11s [id=arn:aws:ecs:us-east-1:123456789012:cluster/my-ecs-cluster]
Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed
And the aws ecs list-clusters command should return the ECS cluster.
~]$ aws ecs list-clusters
{
"clusterArns": [
"arn:aws:ecs:us-east-1:123456789012:cluster/my-ecs-cluster"
]
}
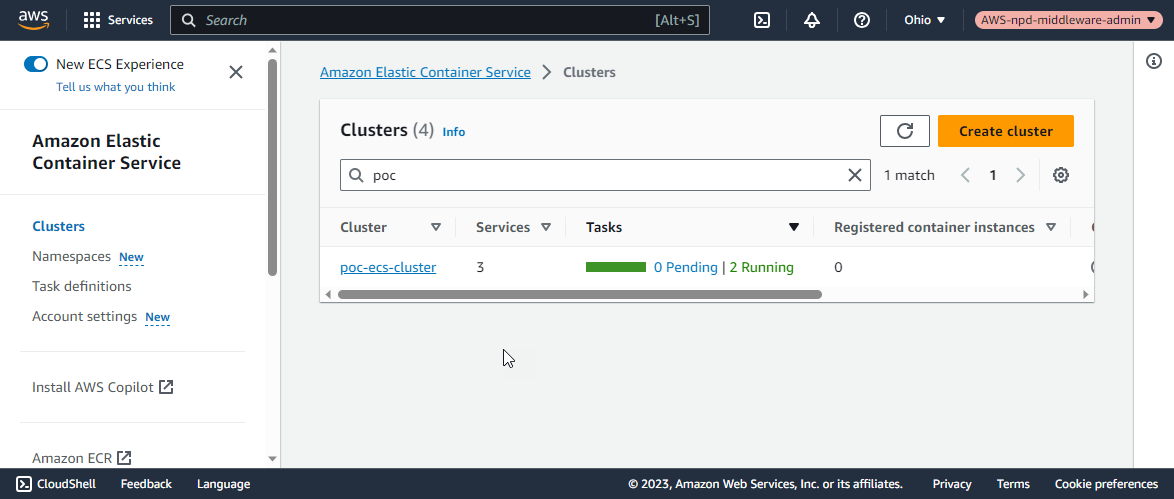
And the ECS cluster should be listed in the AWS console.
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 