
This assumes that you have already installed Samba.
By default, Samba is not configured to share a network drive. Attempting to connect to the share will produce an error.
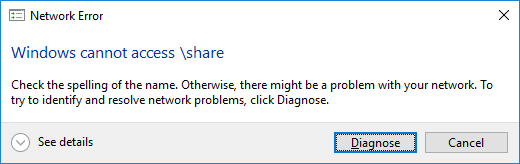
To be able to mount or map the network drive, the /etc/samba/smb.conf file must have the path defined.
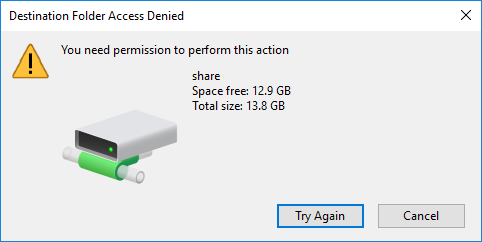
To be able to create new files and modify existing files in the share, the /etc/samba/smb.conf file must have writeable = yes or read only = no. Both these configurations do the same exact thing.
[share]
path = /usr/local/share
writeable = yes
Without writeable = yes, an error will appear when attemtping to create a new file or modify an existing file.
If a CUPS print server is not being used, add the following to prevent a massive number of records in the log with this message: failed to retrieve printer list nt_status_unsuccessful.
printing = bsd
printcap name = /dev/null
Notice in the above example, path is /usr/local/share. If this directory does not exist, create it.
[root@server1 ~]# mkdir -p /usr/local/share
Change the permission to read, write, execute for all users to the share.
[root@server1 ~]# chmod 0777 /usr/local/share
Add a file to the /usr/local/share directory.
[root@server1 ~]# touch /usr/local/share/test1.txt
Ensure Samba is enabled, restart Samba, and ensure Samba is active and running.
[root@server1 ~]# systemctl enable smb
[root@server1 ~]# systemctl restart smb
[root@server1 ~]# systemctl status smb
SELinux
SELinux may be configured to refuse Samba connections. The sestatus command can be used to determine if SELinux is enforcing.
[root@server1 ~]# sestatus
Current mode: enforcing
If SELinux is enforcing, determine the SELinux label on /usr/local/share. In this example, the SELinux type is var_t.
[root@server1 ~]# ls -dZ /usr/local/share
drwxrwxrwx. root root unconfined_u:object_r:var_t:s0 /usr/local/share
Turn on Samba home directories and export read/write.
[root@server1 ~]# setsebool -P samba_enable_home_dirs on
[root@server1 ~]# setsebool -P samba_export_all_rw on
Ensure Samba home directories and export read/write are on.
[root@server1 ~]# /usr/sbin/getsebool -a | grep samba_enable_home_dirs.
samba_enable_home_dirs --> on
[root@server1 ~]# /usr/sbin/getsebool -a | grep samba_export_all_rw.
samba_export_all_rw --> on
Use apt-get, dnf, or yum to install policycoreutils-python. This package contains semanage.
[root@server1 ~]# yum -y install policycoreutils-python
The semanage command can be used to set the /usr/local/share directory and every file and directory below /usr/local/share to have SELinux type samba_share_t. This is a permanent change, meaning this setting will remain in tact after the system is rebooted.
[root@server1 ~]# semanage fcontext -a -t samba_share_t "/usr/local/share(./*)?"
Updates SELinux with these changes.
[root@server1 ~]# restorecon -R -v /usr/local/share
View the SELinux label on /usr/local/share. In this example, the SELinux level should now be samba_share_t instead of var_t.
[root@server1 ~]# ls -dZ /usr/local/share
drwxrwxrwx. root root unconfined_u:object_r:samba_share_t:s0 /usr/local/share
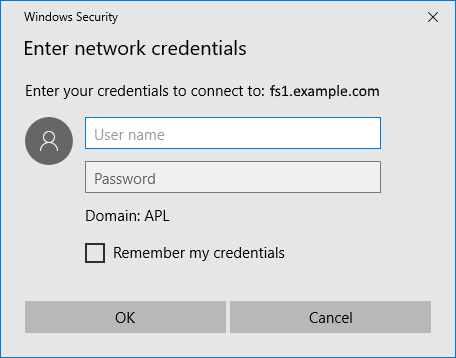
Username / Password
When attempting to connect to the share, there will be a prompt to enter a username and password.
Use the smbpasswd command to add a users password to the SMB database.
[root@server1 ~]# smbpasswd -a john.doe
New SMB password: ********
Retype new SMB password: ********
The pdbedit --list command can be used to verify the user was added to the SMB database.
[root@server1 ~] pdbedit --list
john.doe:1004:
You can now access this share from a different computer in our LAN.
- How to manually connect to a shared network drive using Linux (Mount)
- How to automatically connect to a shared network drive at boot using Linux
- How to map a network drive using Windows
Noperm
If using a Linux client, such as Ubuntu, add the noperm option to the mount command. The noperm option disables permissions check. If noperm is not used, permission denied will likely appear when attempting to write or save files to the share.
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 