
In PowerShell, the $env.computername variable can be used to get the hostname of the system. In this example,
Write-Host $env:computername
Often, you will store the hostname in a variable most likely named $hostname.
$hostname = $env:computername
If you want to append additional text to the hostname, wrap the variable in double quotes.
$hostname = "$env:computername.example.com"
In this example, the computer name is US-H2LXQ72.
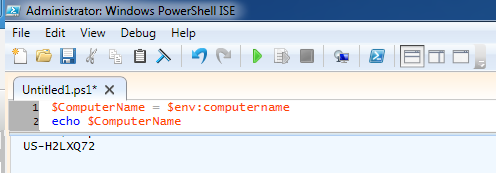
The next set of variables will list the Canonical Name (CN), Organizational Units (OU), and Domain Controller (DC) the computer is in.
$ComputerName = $env:computername
$Filter = "(&(objectCategory=Computer)(Name=$ComputerName))"
$DirectorySearcher = New-Object System.DirectoryServices.DirectorySearcher
$DirectorySearcher.Filter = $Filter
$SearcherPath = $DirectorySearcher.FindOne()
echo $SearcherPath
In this example, the Canonical Name of the computer is US-H2LXQ72, the computer is in the USA > Windows_7 Organizational Unit, and the computer is a member of the Software.Eng.APL domain.
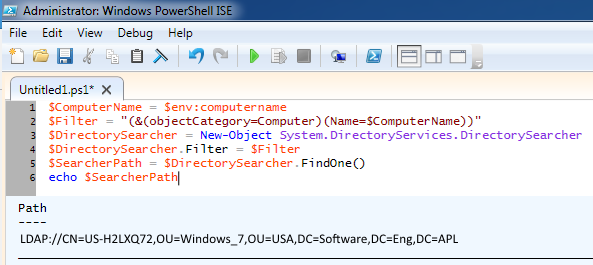
The Distinguished Name variable can be used to remove Path and LDAP from the output.
$ComputerName = $env:computername
$Filter = "(&(objectCategory=Computer)(Name=$ComputerName))"
$DirectorySearcher = New-Object System.DirectoryServices.DirectorySearcher
$DirectorySearcher.Filter = $Filter
$SearcherPath = $DirectorySearcher.FindOne()
$DistinguishedName = $SearcherPath.GetDirectoryEntry().DistinguishedName
echo $DistinguishedName
In this example, the computer named MyHostname is in the Windows10 OU, and the Windows10 OU is a child of the USA OU.
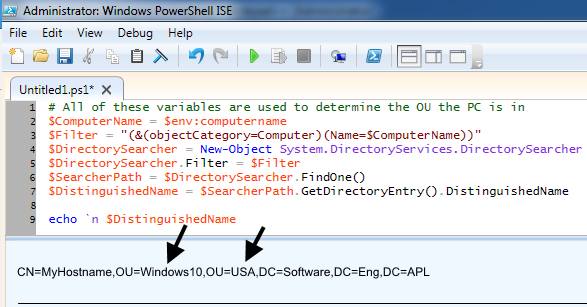
The following can be added to only display the lowest OU the computer is in.
$OUName = ("$DistinguishedName".Split(","))[1]
$OUMainName = $OUName.SubString($OUName.IndexOf("=")+1)
echo "The computer named $($ComputerName) is in the $($OUMainName) OU"
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 