
A servlet is run from an application server such as Tomcat or WebSphere. In this tutorial, we will create a servlet on Tomcat. If you do not have a Tomcat application server setup, follow the instruction in the tutorial on how to install Tomcat.
Create the following directories:
- $tomcat_home/webapps/myApp/src
- $tomcat_home/webapps/myApp/WEB-INF/classes
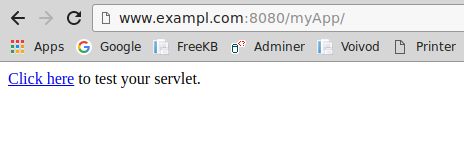
In the $tomcat_home/webapps/myApp directory, create a file named index.html, and add the following markup to the index.html file.
<html>
<body>
<a href="myServlet">Click here</a> to test your servlet.
</body>
</html>
Assuming Tomcat is listening on port 8080, you should now be able to navigate to www.example.com:8080/myApp, and view the index.html page you just created. Next we will create the Java servlet.
In the $tomcat_home/webapps/myApp/src directory, create a file named myServlet.java, and add the following markup to myServlet.java file.
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
@WebServlet("/servlet")
public class myServlet extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("<HTML>");
out.println("<BODY>");
out.println("Hello World. If you are seeing this text, the servlet is working.");
out.println("</BODY>");
out.println("</HTML>");
}
}
Use the javac command to complie myServlet.java into myServlet.class. The -d option is the path to where myServlet.class file will be created. If you are unsure where servlet-api.jar is located, use the find command (find $tomcat_home -iname "servlet-api.jar").
~]# javac
-classpath '/path/to/servlet-api.jar'
-d $tomcat_home/webapps/myApp/WEB-INF/classes
$tomcat_home/webapps/myApp/src/myServlet.java
In the $tomcat_home/webapps/myApp/WEB-INF directory, create a file named web.xml, and add the following markup to web.xml file.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd"
version="3.0">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>myServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>myServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>myServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/myServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
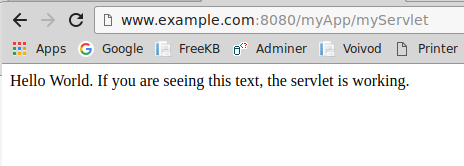
You should now be able to navigate to www.example.com:8080/myApp/myServlet, and the text from the myServlet.class file will be displayed.
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 