
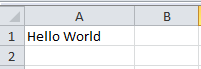
Redirection is all that is needed to create a CSV file in a bash shell script. In this example, a CSV file named example.csv is created, and the text Hello World will be in cell A1 of the CSV file.
~]# echo "Hello World" > example.csv
Comma separate
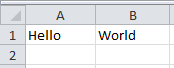
The data in a CSV file is often separated by a comma. Simply placing a comma between Hello and World will separated the data with a comma so that the data is in unique cells.
~]# echo "Hello,World" > example.csv
Or, to do the same in a bash script.
#!/bin/bash
foo="Hello"
bar="World"
echo $foo,$bar > example.csv
Let's say you want data in the cells to be separated by a new line.
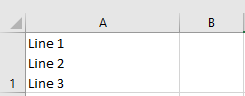
This trick is simply to place double quotes around the data being passed to the CSV file.
#!/bin/bash
foo="Line 1
Line 2
Line 3"
echo "$foo" > example.csv
Tab separate
The column command can be used to create a tab separated CSV file. In this example, the data in the example.csv file is comma separated, and then a new CSV file named tab.csv is created.
~]# column -t example.csv > tab.csv

Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 