
Let's say you use the rabbitmqctl set_parameter command to create a shovel that will move messages from an exchange to a queue.
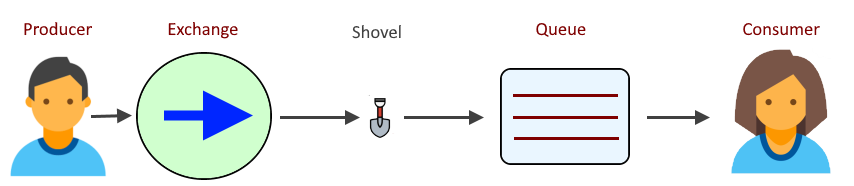
In this example, a shovel named "shovel001" is created that will move messages from the exchange named "exchange001" to the queue named "queue001".
rabbitmqctl set_parameter shovel shovel001
'{
"src-uri": "amqp://john.doe:itsasecret@rabbit001.example.com:5672/%2F",
"src-exchange": "exchange001",
"dest-uri": "amqps://john.doe:itsasecret@rabbit002.example.com:5672/%2F",
"dest-queue": "queue002"
}'
When the source is an exchange, an exclusive queue will be created and the source exchange should be bound to the exclusive queue. An exclusive queue is a sort of temporary queue that will be removed after the shovel is terminated. The exclusive queue will begin with "amq.gen". The rabbitmqctl list_queues command can be used to list the exclusive queues. In this example, there is an exclusive queue in the foo virtual host.
~]$ rabbitmqctl list_queues name exclusive --vhost foo --formatter json | python -m json.tool
[
{
"exclusive": true,
"name": "amq.gen-LuQ1NuuAT1gQ2R-gyeaOIw"
}
]
Likewise, the rabbitmqctl list_bindings command should show that the source exchange is bound to the exclusive queue.
~]# rabbitmqctl list_bindings --vhost foo --formatter json | python -m json.tool
[
{
"arguments": [],
"destination_kind": "queue",
"destination_name": "amq.gen-LuQ1NuuAT1gQ2R-gyeaOIw",
"routing_key": "key002",
"source_kind": "exchange",
"source_name": "exchange001"
}
]
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 