
Flask SQL Alchemy is a library that is intended to make it easy to do something against a database, such as creating a database, creating tables, inserting data, and so on. Instead of having to write complex SQL commands, simple SQL Alchemy directives are used.

First, use the pip install command to install the Flask SQL Alchemy and MariaDB packages.
pip install flask-sqlalchemy
pip install mariadb
Or, you can specify the version to install
pip install flask-sqlalchemy==3.0.2
pip install mariadb==1.1.7
Or, better yet, use a requirements.txt file.
Flask-SQLAlchemy==3.0.5
mariadb==1.1.7
And then install the packages using the requirements.txt file.
pip install --requirement requirements.txt
Let's say the database named "foo" contains a table named "bar" that contains the following record.
~]$ mysql -e "use foo; select * from bar\G"
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
date_created: 2022-10-06
first_name: John
last_name: Doe
Flask uses the MVC (Model View Controller) Framework. Just to make this as obvious as possible, I like my Flask apps to have the following.
- Model -> models.py
- View -> views.py
- Controller -> __init__.py
And let's say your Flask app has the following structure.
├── main.py
├── my-project (directory)
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── views.py
│ ├── models.py
│ ├── templates (directory)
│ │ ├── base.html
│ │ ├── home.html
│ │ ├── results.html
│ └── static (directory)
│ └── custom.css
Let's say __init__.py has the following.
from flask import Flask
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
import mariadb
def app_obj():
app = Flask(__name__,
static_url_path='',
static_folder='static/',
template_folder='templates/')
from .views import views
app.register_blueprint(views, url_prefix='/')
return app
def db_obj(app):
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = 'mariadb+mariadbconnector://john.doe:itsasecret@mariadb.example.com/mydatabase'
app.config["SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS"] = False
db = SQLAlchemy()
db.init_app(app)
return db
def engine_obj(app):
db = db_obj(app)
engine = db.create_engine(app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'])
return engine
def conn_obj(app):
engine = engine_obj(app)
try:
conn = engine.connect()
except mariadb.Warning as warning:
return("Got the following warning when attempting to connect to Mariadb: " + str(warning))
except mariadb.Error as error:
return("Got the following error when attempting to connect to Mariadb: " + str(error))
else:
#Successfully connected to MariaDB"
print("conn = " + str(conn))
return conn
def metadata_obj(app):
db = db_obj(app)
engine = engine_obj(app)
metadata = db.MetaData(bind=engine)
db.MetaData.reflect(metadata)
return metadata
And then views.py could have the following.
from flask import Blueprint, render_template, request, redirect
from flask_mobility import Mobility
from . import app_obj, conn_obj, metadata_obj, close_conn
import mariadb
views = Blueprint('views', __name__)
@views.route('/')
def home():
return render_template('home.html')
@views.route('/Results')
def results():
app = app_obj()
metadata = metadata_obj(app)
conn = conn_obj(app)
mytable = metadata.tables['mytable']
stmt = mytable.select()
result = conn.execute(stmt)
close_conn(app)
return render_template('Results.html', result=result)
And finally, results.html could have something like this.
<p>result = {{ result }}</p>
{% for row in result %}
<p>row = {{ row }}</p>
{% endfor %}
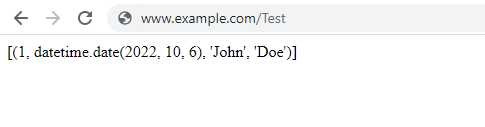
If the select statement is successful, something like this should be returned.
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 