
Flask uses the MVC (Model View Controller) Framework. Just to make this as obvious as possible, I like my Flask apps to have the following.
- Model -> models.py
- View -> views.py
- Controller -> __init__.py
Let's say your Flask app has the following files.
├── main.py
├── database (directory)
│ ├── example.db
├── my-project (directory)
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── views.py
│ ├── models.py
│ ├── templates (directory)
│ │ ├── base.html
│ │ ├── home.html
│ │ ├── results.html
│ └── static (directory)
│ └── custom.css
Let's say your view (views.py in this example) has the following.
from flask import Blueprint
views = Blueprint('views', __name__)
@views.route('/Test')
def test():
return {"foo": "bar"}
Or, jsonify can be used.
from flask import Blueprint, jsonify
views = Blueprint('views', __name__)
@views.route('/Test')
def test():
return jsonify(foo='bar')
In this example, navigating to /Test should return the JSON dictionary.
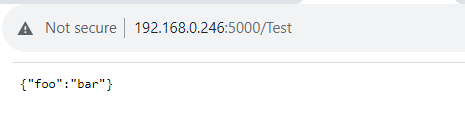
And here is how you could use an if statement based on whether or not the "foo" key contains "bar".
@views.route('/test')
def test():
if my_dict['foo'] == "bar":
return "success"
else:
return "failed"
requests can be used to submit a GET request to an API. First, use the pip install command to install the requests package.
pip install requests
Or, you can specify the version to install
pip install requests==2.28.2
Or, better yet, use a requirements.txt file.
install requests==2.28.2
And then install the packages using the requirements.txt file.
pip install --requirement requirements.txt
In your view, here is how you could submit a GET request to api.example.com/api. Check out my article Python - GET Request for more details on the Python side of this.
import requests
@views.route('/test')
def test():
response = requests.get("http://api.example.com/api")
if response:
print(f"response = {response}")
if response.content:
print(f"response.content = {response.content}")
if response.text:
print(f"response.text = {response.text}")
if response.json():
print(f"response.json = {response.json()}")
print(f"response.json()['foo'] = {response.json()['foo']}")
return render_template('bar.html')
Which should print something like this.
response = <Response [200]>
response.text = {"foo": "hello world"}
reponse.json = {'foo': 'hello world'}
foo = hello world
Here is how you can use the JSON in an if statement.
import requests
@views.route('/test')
def test():
response = requests.get("http://api.example.com/api")
if response.json()['foo'] == "Hello World":
print("foo equals Hello World")
else:
print("foo does not equal Hello World")
return render_template('bar.html')
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 