Linux Commands - regex using awk and gsub


by
Jeremy Canfield |
Updated: November 13 2023
| Linux Commands articles
The awk command is used to only display certain fields of output. In this context, a field is a string of data, delimited by whitespace. For example, the df -h command has fields of data delimited by whitespace.
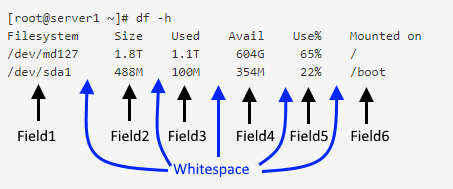
Piping the output to awk '{print}' produces the same exact output.
[root@server1 ~]# df -h | awk '{print}'
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/md127 1.8T 1.1T 604G 65% /
/dev/sda1 488M 100M 354M 22% /boot
gsub can be used to do a regular expression replacement. In this example, "dev" will be replaced with "bar" and $0 is used to only return the results that were modified.
]$ df -h | awk 'gsub("dev", "bar", $0)'
bartmpfs 3.7G 0 3.7G 0% /bar
tmpfs 3.7G 0 3.7G 0% /bar/shm
/bar/mapper/centos_ansible1-root 50G 9.2G 41G 19% /
/bar/mapper/centos_ansible1-home 54G 1.6G 53G 3% /home
/bar/sda1 497M 168M 330M 34% /boot
1 can be included to return all results, both those that were modified and those that were not modified.
]$ df -h | awk 'gsub("dev", "bar", $0) 1'
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
bartmpfs 3.7G 0 3.7G 0% /bar
tmpfs 3.7G 0 3.7G 0% /bar/shm
tmpfs 3.7G 382M 3.3G 11% /run
tmpfs 3.7G 0 3.7G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/bar/mapper/centos_ansible1-root 50G 9.2G 41G 19% /
/bar/mapper/centos_ansible1-home 54G 1.6G 53G 3% /home
/bar/sda1 497M 168M 330M 34% /boot
tmpfs 751M 0 751M 0% /run/user/1000
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 