
This assumes you have already configured the aws command line tool. If not, check out my article on Getting Started with the AWS CLI.
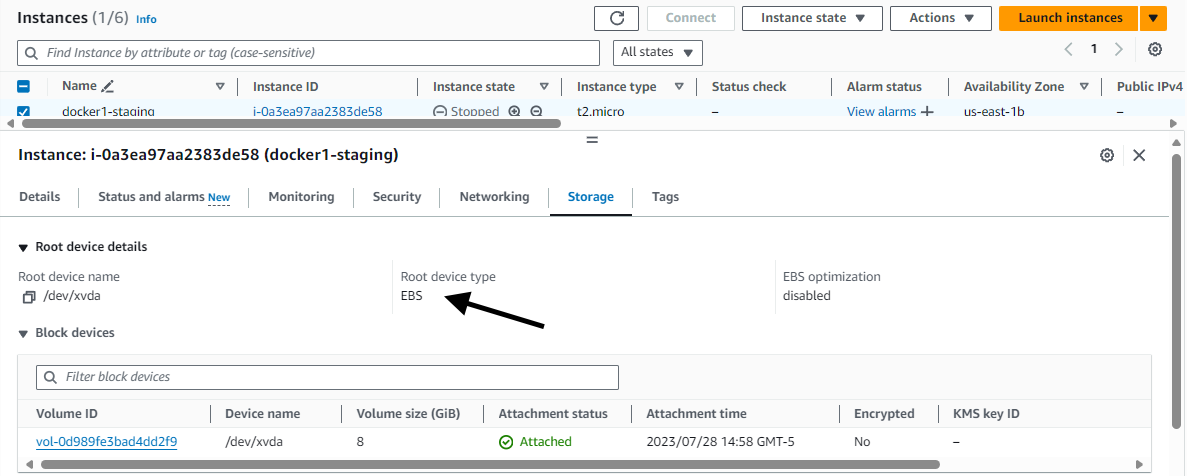
By default, when you create a new EC2 instance, the file system being used by the EC2 instance will be an Elastic Block Storage (EBS) Volume. This can be seen on the Storage tab of your EC2 instance.
The aws ec2 describe-volumes command can be used to list your Elastic Block Storage (EBS) Volumes. Notice in this example that the Elastic Block Storage (EBS) Volume has snapshot snap-096dd96dde7d24189.
~]# aws ec2 describe-volumes
[
{
"AvailabilityZone": "us-east-1b",
"Attachments": [
{
"AttachTime": "2023-07-28T19:58:37.000Z",
"InstanceId": "i-0a3ea97aa2383de58",
"VolumeId": "vol-0d989fe3bad4dd2f9",
"State": "attached",
"DeleteOnTermination": true,
"Device": "/dev/xvda"
}
],
"Encrypted": false,
"VolumeType": "gp3",
"VolumeId": "vol-0d989fe3bad4dd2f9",
"State": "in-use",
"Iops": 3000,
"SnapshotId": "snap-096dd96dde7d24189",
"CreateTime": "2023-07-28T19:58:37.544Z",
"MultiAttachEnabled": false,
"Size": 8
}
]
The aws ec2 describe-snapshots can be used to list your Elastic Block Storage (EBS) Volume Snapshots.
aws ec2 describe-snapshots
And here is an example of how to limit the output using the --query option with SnapshotId.
aws ec2 describe-snapshots --query 'Snapshots[?SnapshotId==`snap-096dd96dde7d24189`]'
And here is an example of how to limit the output using the --query option with VolumeId.
aws ec2 describe-snapshots --query 'Snapshots[?VolumeId==`vol-0d989fe3bad4dd2f9`]'
Something like this should be returned
[
{
"Description": "",
"Encrypted": false,
"OwnerId": "123456789012",
"Progress": "100%",
"SnapshotId": "snap-096dd96dde7d24189",
"StartTime": "2023-07-25T22:43:53.821000+00:00",
"State": "completed",
"VolumeId": "vol-0d989fe3bad4dd2f9",
"VolumeSize": 8,
"OwnerAlias": "amazon",
"StorageTier": "standard"
}
]
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 