
There is both a frontend that listens for connections on port 3000 by default and a backend that listens for connections on port 7007 by default.
If you are using Node.js version 20 or higher.
]$ node --version
v20.18.1
You'll need to set the --no-node-snapshot option.
export NODE_OPTIONS=--no-node-snapshot
The yarn start command to start the frontend in the foreground.
~]$ yarn start
Loaded config from app-config.yaml
<i> [webpack-dev-server] Project is running at:
<i> [webpack-dev-server] Server: http://localhost:3000/
<i> [webpack-dev-server] On Your Network (IPv4): http://10.11.12.13:3000/
<i> [webpack-dev-server] Content not from webpack is served from '/home/john.doe/backstage/packages/app/public' directory
<i> [webpack-dev-server] 404s will fallback to '/index.html'
webpack compiled successfully
And we should be able to see our backstage app at http://<hostname or IP address>:3000/.
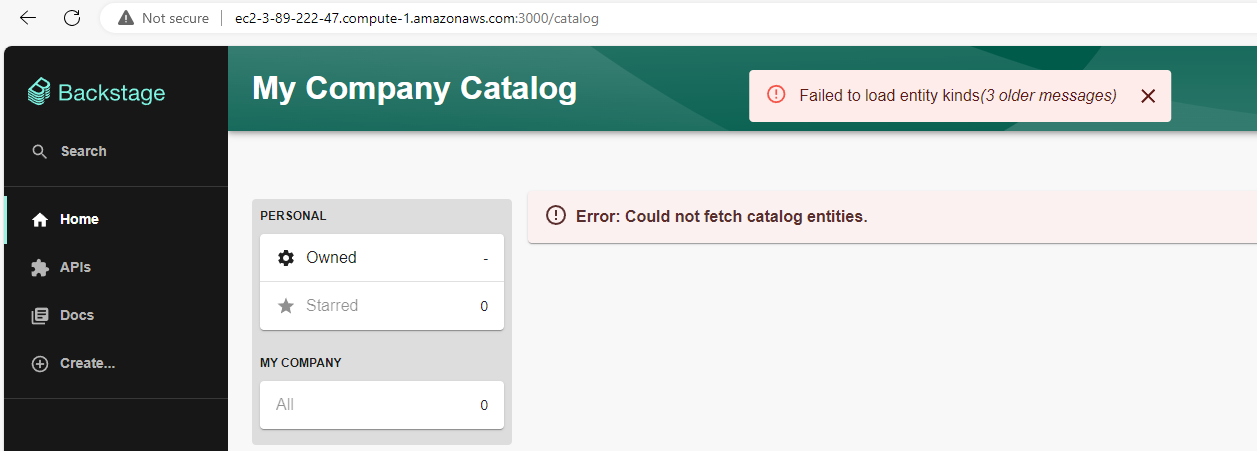
But if we click on the Enter button, "Failed to load entity kinds" and "Could not fetch catalog entities" will be displayed because the Backstage backend has not been started.
Let's use the yarn start-backend command to start the backend.
yarn start-backend
Or you can run backstage in the background so you can continue to use the console.
yarn start &
yarn start-backend &
netstat can be used to ensure the frontend is listening for connections on port 3000 and the backend is listening for connections on port 7007.
~]# netstat -anop |egrep '3000|7007'
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 5780/node off (0.00/0/0)
tcp6 0 0 :::7007 :::* LISTEN 6494/node off (0.00/0/0)
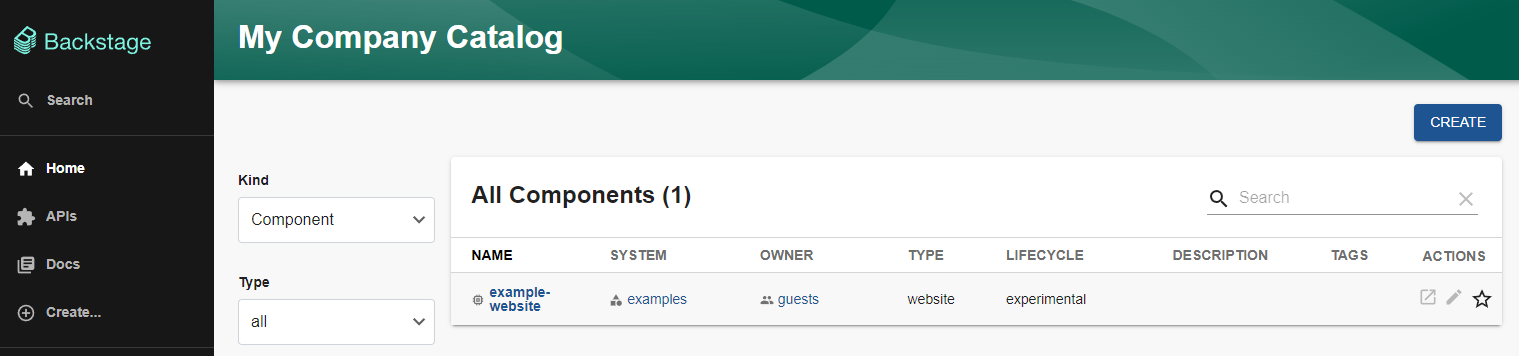
Now, when we go to http://<hostname or IP address>:3000/ and hit the Enter button, if you see example-website this means the frontend is able to talk to the backend. In other words, it works!
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 