
This assumes:
- You have an ArgoCD server up and running. If not, check out my article Install Red Hat OpenShift GitOps Operator using the console (Argo CD)
- You have installed the ArgoCD CLI.
- You are able to log into ArgoCD using the CLI. If not, check out my article Log into ArgoCD using the CLI on OpenShift
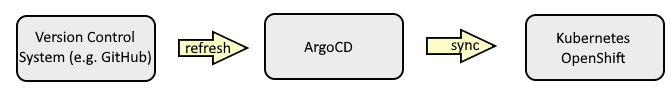
ArgoCD sits between your version control system (such as GitHub) and your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters and is used to create resources (such as deployments, pods, services, routes, config maps and secrets) in a particular namespace in your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters. Almost always, this means you will have YAML files for your various Kubernetes or OpenShift resources in your version control system, such as YAML files for your Kubernetes or OpenShift deployments, YAML files for your Kubernetes or OpenShift secrets, YAML files for your Kubernetes or OpenShift services, et cetera, and ArgoCD will create the corresponding resources in your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters using the YAML files in your version control system. ArgoCD will also ensure the resources on your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters remain in sync with their corresponding YAML files in your version control system.
The argocd admin cluster namespaces command can be used to list the namespaces in each cluster that ArgoCD manages.
~]$ argocd admin cluster namespaces
CLUSTER NAMESPACES
https://kubernetes.default.svc
https://api.prod.op.example.com:6443 foo,datadog,bar,hello-world (total 11)
https://api.dev.op.example.com:6443 foo,datadog,bar,hello-world (total 13)
https://api.stage.op.example.com:6443 foo,datadog,bar,hello-world (total 16)
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 