
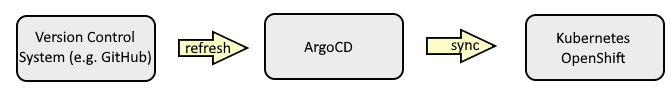
ArgoCD sits between your version control system (such as GitHub) and your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters and is used to create resources (such as deployments, pods, services, routes, config maps and secrets) in a particular namespace in your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters. Almost always, this means you will have YAML files for your various Kubernetes or OpenShift resources in your version control system, such as YAML files for your Kubernetes or OpenShift deployments, YAML files for your Kubernetes or OpenShift secrets, YAML files for your Kubernetes or OpenShift services, et cetera, and ArgoCD will create the corresponding resources in your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters using the YAML files in your version control system. ArgoCD will also ensure the resources on your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters remain in sync with their corresponding YAML files in your version control system.
Let's say you have multiple repos, perhaps something like this.
https://github.com/acme/foo.git
https://github.com/acme/bar.git
https://github.com/acme/hello.git
https://github.com/acme/world.git
And each of these repos can be added to ArgoCD using the same credentials, such as the same username and password.
argocd repo add https://github.com/acme/foo.git --username john.doe --password itsasecret
argocd repo add https://github.com/acme/bar.git --username john.doe --password itsasecret
argocd repo add https://github.com/acme/hello.git --username john.doe --password itsasecret
argocd repo add https://github.com/acme/world.git --username john.doe --password itsasecret
Or the same token.
argocd repo add https://github.com/acme/foo.git --username ' ' --password 'ghp_ggEVZkS0N2mzlGABCK0pO3C123CSmS0oFNeX'
argocd repo add https://github.com/acme/bar.git --username ' ' --password 'ghp_ggEVZkS0N2mzlGABCK0pO3C123CSmS0oFNeX'
argocd repo add https://github.com/acme/hello.git --username ' ' --password 'ghp_ggEVZkS0N2mzlGABCK0pO3C123CSmS0oFNeX'
argocd repo add https://github.com/acme/world.git --username ' ' --password 'ghp_ggEVZkS0N2mzlGABCK0pO3C123CSmS0oFNeX'
Or the same SSH key.
argocd repo add git@github.com:acme/foo.git --ssh-private-key-path $HOME/.ssh/argocd
argocd repo add git@github.com:acme/bar.git --ssh-private-key-path $HOME/.ssh/argocd
argocd repo add git@github.com:acme/hello.git --ssh-private-key-path $HOME/.ssh/argocd
argocd repo add git@github.com:acme/world.git --ssh-private-key-path $HOME/.ssh/argocd
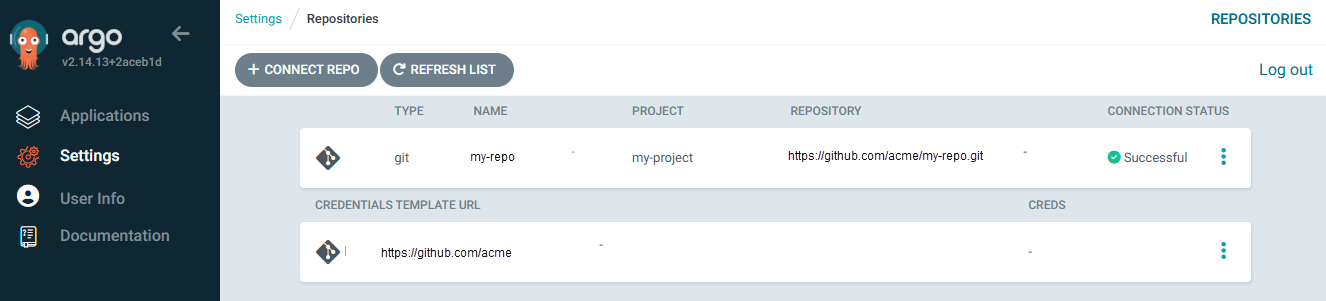
This is a good scenario to add a Credential Template to ArgoCD so that when adding repo's to ArgoCD you don't need to include the username and password or token or SSH key and instead the repo will be added using the Credential Template. The argocd repocreds list command can be used to list the Credential Template that have been added to ArgoCD..
~]$ argocd repocreds list
URL PATTERN USERNAME SSH_CREDS TLS_CREDS
https://github.com/acme false false
Or in the ArgoCD console at Settings > Repositories.
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 