
Remote queues are used so that you can create a connection between a queue on machine 1 (the sender) and machine 2 (the receiver). Before setting up remote queue, you will need to create a queue manager on both machine 1 and machine 2, and a local transmission queue on machine 1 (the sender) should already have been created.

If using MQ Explorer
On machine 1 (the sender), create a remote queue definition.
- In the left panel of MQ Explorer, expand Queue Managers > Machine 1 (the sender) Queue Manager.
- Right-click on the Queues folder and select New > Remote Queue Definition.
- In the Name field, give your remote queue definition a name, such as Q01, and select Next.
- In the Remote queue manager field, enter the name of the queue manager on machine 2 (the receiver).
- In the Transmission queue field, enter the name of the queue manager on machine 2 (the receiver).
- Select Finish.
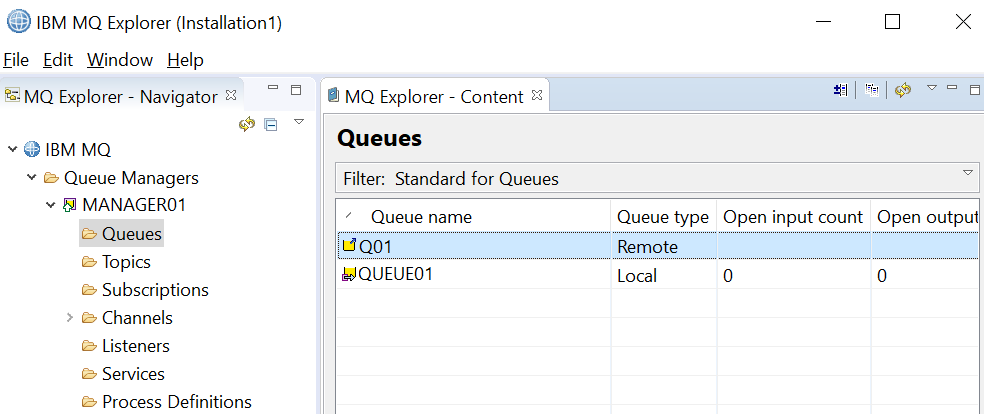
The remote queue definition should now be displayed.
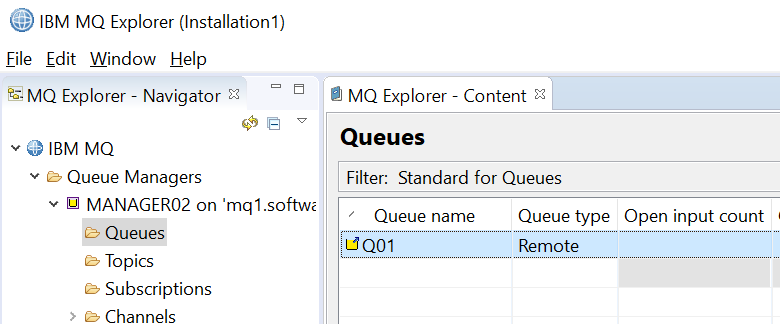
On machine 2 (the receiver), create a remote queue.
- TBD
In this example, the remote queue is now displayed.
If using Linux command line
The steps on how to setup machine 1 are TBD.
On machine 2 (the receiver), switch to the mqm user.
su - mqm
Create a remote queue. In this example, the remote queue is named QUEUE02, on queue manager MANAGER02.
echo "define qremote (Q01) rname (Q01) rqmname(MANAGER02) xmitq (MANAGER02)" | runmqsc MANAGER01
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 