
If you are not familiar with the oc command, refer to OpenShift - Getting Started with the oc command.
There are a few different ways to run a pod on a specific node.
- Using nodeSelector
- Nodes are labeled with a key=value (e.g. region=east)
- If namespace node-selector is an exact match of a nodes key=value label, then the pod can be scheduled run on the node
- If a pods nodeSelector is an exact match of a nodes key=value label, then the pod can be scheduled run on the node
- Using nodeAffinity (this article)
- Nodes are labeled with a key=value (e.g. region=east)
- If a pods nodeAffinity regular expression matches a nodes key=value label, the pod can be scheduled to run on the node
- Using podAffinity
- Pods are labeled with a key=value (e.g. region=east)
- If a pods podAffinity regular expression matches another pods key=value label, the pod can be scheduled to run on the same node that the other pods is running on
- Using Taint and Toleration
- Nodes are labeled with a key=value:taint (e.g. region=east:NoSchedule)
- If a pods tolerations uses Exists and the pods tolerations key matches the nodes toleration key, the pod is allowed to run on the node
- If a pods tolerations uses Equal and the pods tolerations key and value is an exact match of the nodes tolerations key and value, the pod is allowed to run on the node
The oc new-app command is used to deploy an application. There are various ways to deploy an app.
- From GitHub (https://github.com)
- From Docker Hub (https://hub.docker.com)
- From an image
- From a build
- From a JSON or YAML file (templates)
The scheduler is responsible for determining which worker node a resource should get created on. For example, when deploying a new application to OpenShift, the scheduler determines which worker node the pod should be created on, typically the worker node with the most available memory and CPU. Check out my article on the default scheduler.
The oc get nodes command will return the list of nodes. Notice there are two worker nodes.
~]# oc get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
my-node-infra-4k6z9 Ready infra 273d v1.11.0+d4cacc0
my-node-master-0 Ready master 273d v1.11.0+d4cacc0
my-node-worker-5n4fj Ready worker 273d v1.11.0+d4cacc0
my-node-worker-v8r9r Ready worker 273d v1.11.0+d4cacc0
Let's say you want to be able to specify the worker node that an application / container / deployment / pod will run. To accomplish this, you will need to label the worker nodes. The oc label node command can be used to apply one or more labels to a worker node. The worker node doesn't have to be labeled "region". You can pick any key value pair you would like.
~]$ oc label node my-node-worker-5n4fj region=east
node/my-node-worker-5n4fj labeled
~]$ oc label node my-node-worker-v8r9r region=west
node/my-node-worker-v8r9r labeled
Or in the OpenShift console, at Compute > Nodes you can edit a nodes labels.
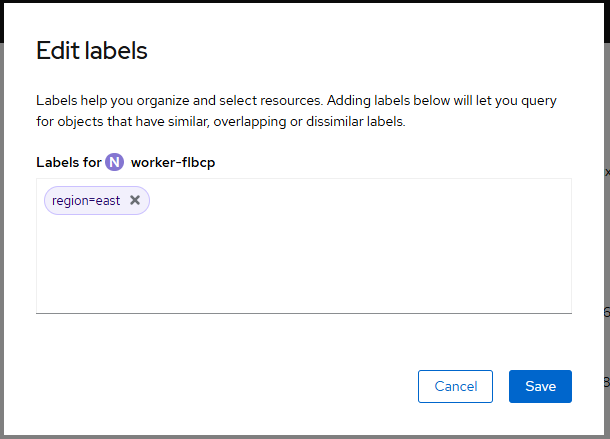
The oc describe node command can be used to see the labels that have been applied to the worker nodes.
~]$ oc describe node my-node-worker-5n4fj
Name: my-node-worker-5n4fj
Roles: infra,worker
Labels: region=east
~]$ oc describe node my-node-worker-v8r9r
Name: my-node-worker-v8r9r
Roles: infra,worker
Labels: region=west
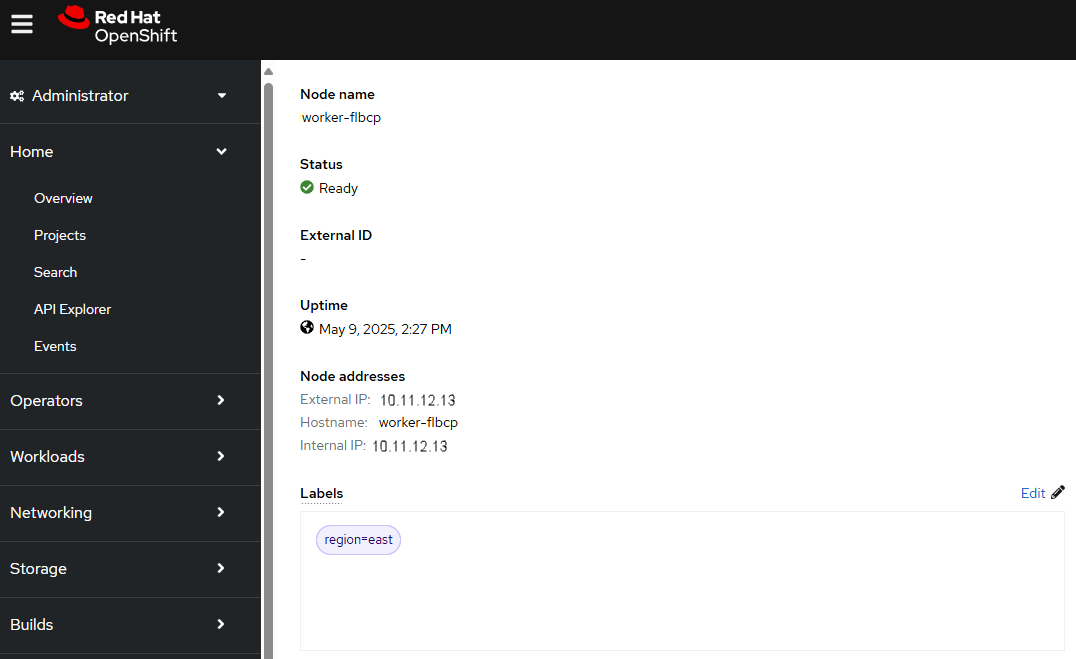
Or in the OpenShift console, at Compute > Nodes you can view a nodes labels.
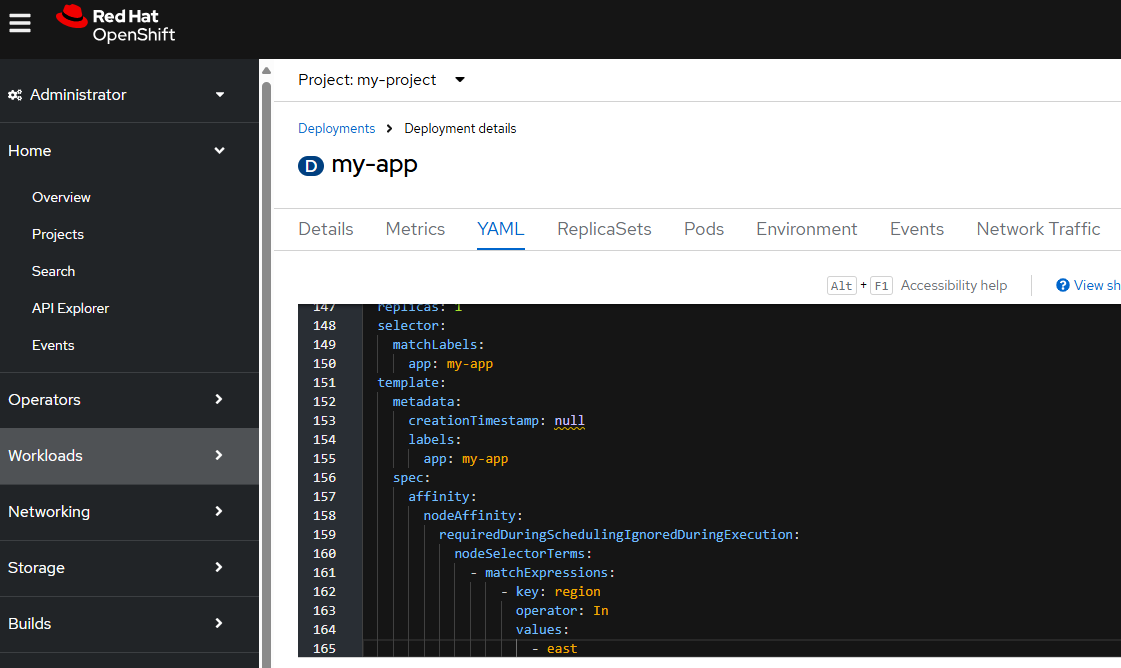
Here is an example of what you could have in your deployment YAML to have the pod created on the "east" or "west" worker node using nodeAffinity.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: my-deployment
spec:
template:
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: region
operator: In
values:
- east
Or in the OpenShift console at Workloads > Deployments > your deployment > YAML.
With nodeAffinity, the scheduling of a pod on a node can either be preferred or required. Execution basically means "running pods" thus IgnoredDuringExecution means that nodeAffinity will have no impact on currently running pods. On the other hand, with Taint and Toleration, NoExecute can be used to terminate running pods.
- preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution
- requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution
The following operators can be used with matchExpression.
- In (worker node label contains one of the listed key:value pairs)
- NotIn (worker node label does not contain one of the listed key:value pairs)
- Exists (worker node label is an exact made of the key, not the value)
- DoesNotExist (worker node label is not an exact made of the key)
- Lt (worker node label is less than)
- Gt (worker node label is greater than)
Here is an example of how Exists would be used. In this example, if the node is labeled with key "region" the pod will be created on the node that has the "region" key.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: my-deployment
spec:
template:
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: region
operator: Exists
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 