
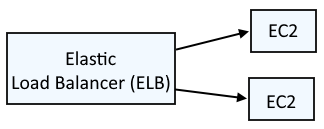
An Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) is typically used to load balance requests across two (or more) different EC2 instances.
This assumes you have setup Terraform with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) provider. If not, check out my article Amazon Web Services (AWS) Getting Started with Terraform.
Let's say you have the following files on your Terraform server.
├── required_providers.tf
├── network_load_balancers (directory)
│ ├── elastic_ips.tf
│ ├── listener.tf
│ ├── load_balancer.tf
│ ├── provider.tf
│ ├── target_group.tf
│ ├── virtual_private_clouds.tf
required_providers.tf will almost always have this.
terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
}
}
}
Let's say provider.tf has the following. In this example, the "default" profile in /home/username/.aws/config and /home/username/.aws/credentials is being used. This assumes you have setup Terraform as described in Amazon Web Services (AWS) - Getting Started with Terraform.
provider "aws" {
alias = "default"
profile = "default"
region = "default"
}
And virtual_private_clouds.tf could have the following. Replace "my-vpc" with the name of your Virtual Private Cloud. Check out my articles list Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) using Terraform and list Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) Subnets using Terraform for more details on this.
data "aws_vpc" "my_vpc" {
filter {
name = "tag:Name"
values = ["my-vpc"]
}
}
data "aws_subnet" "my_aws_subnet" {
filter {
name = "tag:Name"
values = ["us-east-1a"]
}
}
And elastic_ips,tf. could have the following to get your Elastic IPs. Check out my article list Elastic IP Addresses (EIP) using Terraform for more details on this.
data "aws_eips" "staging_eips" {
tags = {
environment = "staging"
}
}
And load_balancer.tf could have the following to create a Network Load Balancer.
resource "aws_lb" "my-network-load-balancer" {
name = "my-network-load-balancer"
internal = false
load_balancer_type = "network"
subnet_mapping {
subnet_id = data.aws_subnet.my_aws_subnet.id
allocation_id = data.aws_eips.staging_eips.elastic_ip_allocation_id
}
tags = {
Environment = "staging"
Name = "my-network-load-balancer"
}
}
And target_group.tf could have the following to create the network load balancer target group.
resource "aws_lb_target_group" "my-target-group" {
name = "my-target-group"
port = 80
protocol = "HTTP"
vpc_id = data.aws_vpc.my_vpc.id
tags = {
Name = "my-target-group"
}
}
And listener.tf could have the following to create the network load balancer listener.
resource "aws_lb_listener" "my-listener" {
load_balancer_arn = aws_lb.my-network-load-balancer.arn
port = 80
protocol = "TCP"
default_action {
type = "forward"
target_group_arn = aws_lb_target_group.my-target-group.arn
}
tags = {
Name = "my-listener"
}
}
The terraform plan command can be used to see what Terraform will try to do.
terraform plan
And the terraform apply command can be used to create the Elastic Load balancer Target Group.
terraform apply
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 