
If you are not familiar with the oc command, refer to OpenShift - Getting Started with the oc command.
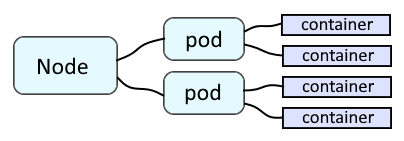
A node contains one or more pods, and each pod contains one or more containers.
The oc get pods command can be used to list the pods in the currently selected project / namespace.
TIP
The -A or --all-namespaces flag can be used to list the limits in every project / namespace.
The -n or --namespace flag can be used to list the limits in a certain project / namespace.
In this example, the currently selected project does not contain any pods.
~]# oc get pods
No resources found.
On the other hand, if your selected project contains one or more pods, something like this should be returned.
~]# oc get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
foo-9mzm2 1/1 Running 0 8d
foo-vmzmz 1/1 Running 0 8d
bar-pflxc 1/1 Running 0 8d
If you do not want to use the -n or --namespace command line option, you can select a project and then issue the oc get pods command without the -n option.
~]# oc get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
foo-9mzm2 1/1 Running 0 8d
foo-vmzmz 1/1 Running 0 8d
bar-pflxc 1/1 Running 0 8d
The --output wide option can be used to include addtional fields.
~]# oc get pods --output wide --namespace my-project
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED MODE
foo-9mzm2 1/1 Running 0 8d 10.142.118.51 worker-hsjrp <none>
foo-vmzmz 1/1 Running 0 8d 10.142.118.52 worker-v8r9r <none>
bar-pflxc 1/1 Running 0 8d 10.142.118.53 worker-ab9df <none>
And here is how to view the pods in a specific node.
~]# oc get pods --all-namespaces --field-selector spec.nodeName=dev001-worker-5n4fj
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
project001 foo-9mzm2 1/1 Running 0 84d
project001 foo-vmzmz 1/1 Running 0 84d
project002 bar-pflxc 1/1 Running 0 84d
The -o or --output option and custom-columns can be used to customize the columns that are returned. In this example, only the pod and node names will be returned.
~]$ oc get pods --output custom-columns=POD:.metadata.name,NODE:.spec.nodeName,STATE:.status.phase
POD NODE STATE
foo-9mzm2 worker-84928 Running
foo-vmzmz worker-pcl22 Running
bar-pflxc worker-8wjg7 Completed
--no-headers can be used if you don't want the headers.
~]$ oc get pods --output custom-columns=POD:.metadata.name,NODE:.spec.nodeName,STATE:.status.phase --no-headers
foo-9mzm2 worker-84928 Running
foo-vmzmz worker-pcl22 Running
bar-pflxc worker-8wjg7 Completed
The -o json or -o yaml option can be used to show the pods JSON or YAML file.
oc get pod foo-vmzmz -o yaml
Let's say the pod label has the following selector.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: my-pod
Here is an example of how you can use selector to return the pods matching a label.
~]$ oc get pods --namespace my-project --selector=app.kubernetes.io/name=my-pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
my-pod-7744cbb479-7w8xd 1/1 Running 0 3d6h
If you create a pod and deploy an app using the oc new-app command, something like this should be displayed.
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
foo-vmzmz 0/1 Init:0/2 0 15s
The oc describe pod command can be used to show more details for a pod. Or, the oc get pods command with the --output json or --output yaml option can be used.
~]$ oc describe pod hello-openshift
Name: hello-openshift
Namespace: foo
Priority: 0
Node: worker-hsjrp/10.84.188.68
Start Time: Tue, 26 Jul 2022 07:22:41 -0500
Labels: name=hello-openshift
openshift.io/scc: anyuid
Status: Pending
IP: 10.131.5.175
IPs:
IP: 10.131.5.175
Containers:
hello-openshift:
Container ID:
Image: openshift/hello-openshift
Image ID:
Port: 8080/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
State: Waiting
Reason: ImagePullBackOff
Ready: False
Restart Count: 0
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/tmp from tmp (rw)
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from kube-api-access-8vzd8 (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready False
ContainersReady False
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
tmp:
Type: EmptyDir (a temporary directory that shares a pod's lifetime)
Medium:
SizeLimit: <unset>
kube-api-access-8vzd8:
Type: Projected (a volume that contains injected data from multiple sources)
TokenExpirationSeconds: 3607
ConfigMapName: kube-root-ca.crt
ConfigMapOptional: <nil>
DownwardAPI: true
ConfigMapName: openshift-service-ca.crt
ConfigMapOptional: <nil>
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: node-type=general
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
Events:
<none>
The --output jsonpath option can be used to print the value of a specific JSON key.
~]$ oc get pod hello-openshift --output jsonpath={.status.hostIP}
10.84.188.68
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 