
If you are not familiar with the oc command, refer to OpenShift - Getting Started with the oc command.
I like to think of a machine as OpenShift representation of a Virtual Machine, such as an Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2 Instance, or a VMWare Virtual Machine, and then a Node, and then the pods running on the node. Machine Configs can be used to configure the Virtual Machine Operating System, such as configuring a Linux systemd service such as sshd or chronyd or Network Manager.
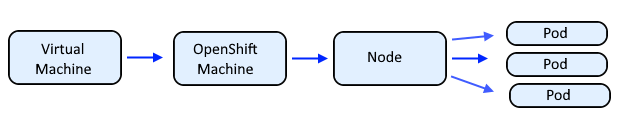
A Machine Set is used to create machines with certain default configurations, such as 4 CPUs.
The oc get machinesets command can be used to display the desired, current, ready and available count for a certain type of machine, in the openshift-machine-api namespace.
~]$ oc get machinesets --namespace openshift-machine-api
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AVAILABLE AGE
my-cluster-edge 2 2 2 2 140d
my-cluster-infra 3 3 3 3 140d
my-cluster-worker 2 2 2 2 143d
The output option can be used to output the YAML for each machine set.
oc get machineset/my-cluster-worker --namespace openshift-machine-api --output yaml
Which should return YAML that looks something like this. Notice in this example that there are 2 replicas, thus this machine set will ensure there are always 2 machines.
apiVersion: machine.openshift.io/v1beta1
kind: MachineSet
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2021-07-16T17:10:51Z"
generation: 4
labels:
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-cluster: my-cluster
name: my-cluster-worker
namespace: openshift-machine-api
resourceVersion: "485196036"
uid: 57d19e1d-6533-4a76-ad21-f5109e18f357
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-cluster: my-cluster
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-machineset: my-cluster-worker
template:
metadata:
labels:
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-cluster: my-cluster
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-machine-role: worker
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-machine-type: worker
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-machineset: my-cluster-worker
spec:
lifecycleHooks: {}
metadata:
labels:
node-role.kubernetes.io/compute: ""
node-type: general
providerSpec:
value:
apiVersion: vsphereprovider.openshift.io/v1beta1
credentialsSecret:
name: my-secret
diskGiB: 120
kind: VSphereMachineProviderSpec
memoryMiB: 65536
metadata: {}
network:
devices:
- networkName: my-network
numCPUs: 4
numCoresPerSocket: 1
snapshot: ""
template: my-cluster-rhcos
userDataSecret:
name: worker-user-data
workspace:
datacenter: my-datacenter
datastore: my-datastore
folder: /foo/bar
resourcePool: /foo/barb/Resources
server: server1.example.com
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 