
The default router, which is in the openshift-ingress project / namespace, is used to route requests coming into the OpenShift cluster to their appropriate pods / services. The default router uses an HAProxy (High Availability Proxy) Load Balancer to route requests to their appropriate pods / services.
The oc get pods command can be used to list the pods in the openshift-ingress project / namespace.
~]$ oc get pods --namespace openshift-ingress
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
router-default-6f84fdff65-4zdmp 1/1 Running 0 57d
router-default-6f84fdff65-t7h22 1/1 Running 0 57d
router-default-6f84fdff65-z579b 1/1 Running 0 57d
Let's say you have deployed the hello openshift application, and you have created a route and a service for the Hello Openshift application. The oc get routes command will give you the URL for the route, which is http://hello-openshift-default.apps.openshift.example.com:8080 in this example.
~]$ oc get routes
NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD
hello-openshift hello-openshift-default.apps.openshift.example.com hello-openshift 8080 None
A route or an ingress object is used to route a request onto a service, which is then routed onto a pod, and then to the container in the pod, and finally to the application running in the container.
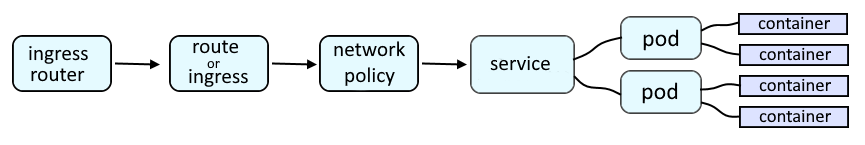
In this example, the oc expose service command would have been used to create the route which would have also configured the default router to know that requests submitted with http://hello-openshift-default.apps.openshift.example.com:8080 should be routed to the Hello Openshift application, which under the hood can be seen in the haproxy.config file in the default router pod.
oc exec pod/router-default-6b97d59988-cscw4 -- cat haproxy.config
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 