
If you are not familiar with the oc command, refer to OpenShift - Getting Started with the oc command.
- Limits can be used to set the minimum and maximum amount of CPU/memory/storage for:
- a single deployment related asset (e.g. container / pod) in a namespace and is typically defined in deployment YAML or deployment config YAML
- all deployment related assets (e.g. containers / pods) in a namespace
You can set both requests and limits.
- requests
- the amount of memory / CPU that is reserved for containers / pods. For example, if a node has 10 GB of memory and a pod requests 1 GB of memory, then 1 of the 10 GB of memory on the node would be reserved for the pod, meaning the node would then have 9 remaining GB of memory for other containers / pods. This is why it's important that containers / pods only request the minimum amount of CPU / memory that the container / pod require.
- limit
- the maximum amount of memory / CPU a container can use
- if a container reaches the CPU limit, the container will be throttled (won’t let it consume any more CPU)
- if a container reaches the memory limit, Out Of Memory (OOM) should occur and the pod should be killed
- if a container reaches the storage limit, the pod should be evicted
Before configuring Requests and Limits for CPU and memory, you will probably want to
- determine the average amount of CPU and memory being used by pods
- determine the amount of CPU and memory available on your nodes
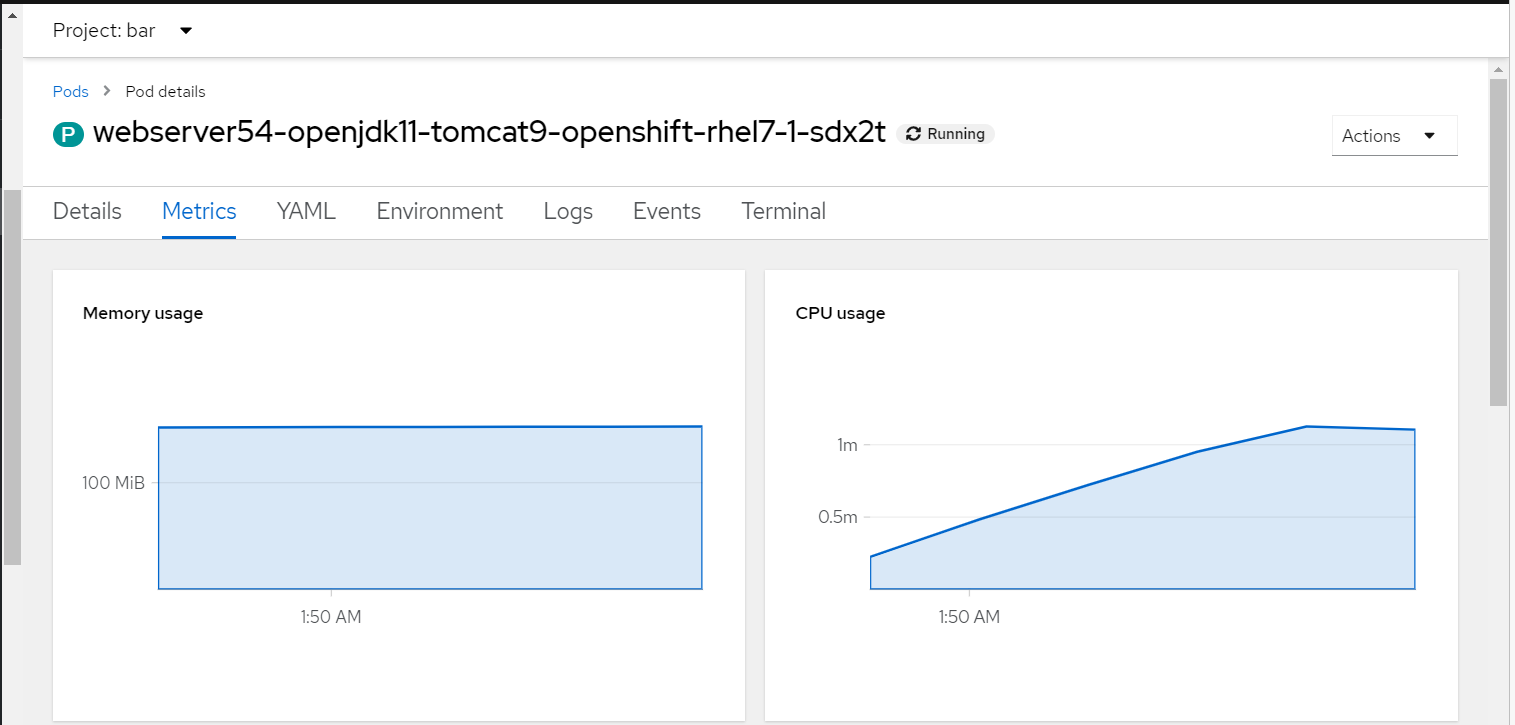
Check out my article FreeKB - OpenShift - CPU and memory usage. For example, in the OpenShift console at Workloads > pods > pod > Metrics you can get a general idea the amount of memory and CPU being used by the pod.
Let's say you have a YAML file named limits.yml that contains the following markup.
This will set the combined CPU and memory limits of all of the containers or pods in a project. If you want to limit the CPU and memory for a single deployment / container / pod in a namespace, refer to Deploy an application with CPU Memory limits using a YAML template file.
apiVersion: v1
kind: LimitRange
metadata:
name: my-limits
spec:
limits:
- type: Pod
max:
cpu: 20m
memory: 1Gi
min:
cpu: 200m
memory: 6Mi
- type: Container
max:
cpu: 2
memory: 1Gi
min:
cpu: 100m
memory: 4Mi
default:
cpu: 300m
memory: 200Mi
defaultRequest:
cpu: 200m
memory: 100Mi
maxLimitRequestRatio:
cpu: 10m
The oc apply or oc create command with the -f or --filename option can be used to create the limits using the template JSON or YAML file.
The oc replace command can be used to replace limits using a new or updated template JSON or YAML file.
The oc edit command can be used to update a limits template YAML file.
~]$ oc create --filename limits.yml
limitrange/my-limits created
The oc get limits command can be used to list the limits that have been created in the current project / namespace.
~]$ oc get limits
NAME CREATED AT
my-limits 2022-07-26T12:25:53Z
The oc describe limits command can be used to display more details about a limit.
- requests - the minimum of CPU/memory that is reserved or allocated for the container
- limits - the maximum amount of CPU/memory that can be used by the container
~]$ oc describe limits my-limits
Name: my-limits
Namespace: foo
Type Resource Min Max Default Request Default Limit Max Limit/Request Ratio
---- -------- --- --- --------------- ------------- -----------------------
Pod cpu 200m 2 - - -
Pod memory 6Mi 1Gi - - -
Container cpu 100m 2 200m 300m 10
Container memory 4Mi 1Gi 100Mi 200Mi -
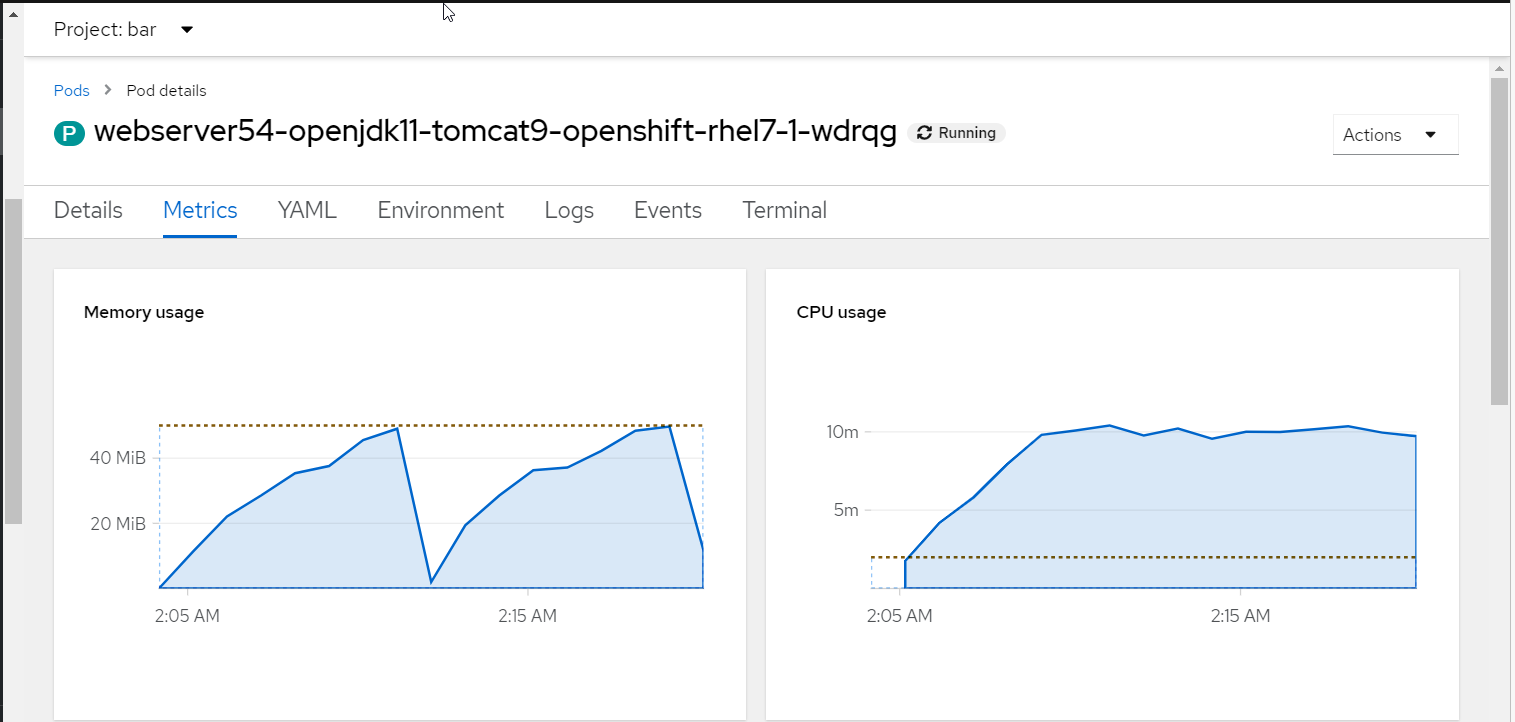
And in the OpenShift console, you should see a dotted line representing the limit. I tend to noticed that memory is never exceeded but CPU can be forgiving, where a pod may exceeded the max CPU limit.
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 