
Let's say you have deployed an application to OpenShift, and when requesting the application, Connection timed out is being returned.
Failed connect to my-route-my-project.apps.openshift.example.com; Connection timed out
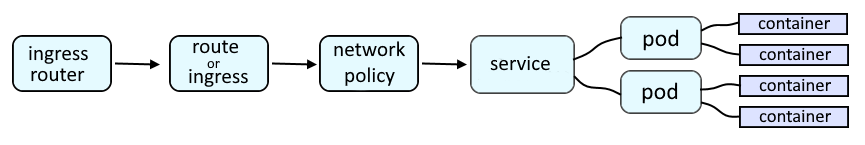
An OpenShift route or an Ingress route will provide a URL such as http://my-route-my-project.apps.openshift.example.com which is used to route a request onto a service, which is then routed onto a pod, and then to the container in the pod, and finally to the application running in the container.
The oc get pods command can be used to determine if the pod is Running.
~]# oc get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
my-pod-9mzm2 1/1 Running 0 8d
my-pod-zm5g6 1/1 Running 0 8d
Use the oc describe pod command to determine the ports the pod is listening for connections on.
~]$ oc describe pod my-pod-zm5g6
Containers:
my-app:
Ports: 8080/TCP
If there are two (or more pods) in the namespace, the oc exec and curl command can be used to determine if one of the other pods is able to get a response from the pod with that is returning connection timed out.
~]$ oc exec pod/my-pod-9mzm2 -- curl --silent --insecure my-pod-zm5g6:8080 -v
* About to connect() to my-pod-zm5g6 port 8080 (#0)
* Trying my-pod-zm5g6...
* Connected to my-pod-zm5g6 (10.131.4.136) port 8080 (#0)
> Host: my-pod-zm5g6:8080
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
If connection timed out is returned, check to see if a network policy is denying ingress. The oc get networkpolicies command can be used. In this example, no pods are allowed ingress.
~]$ oc get networkpolicy deny-ingress -o yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: deny-ingress
namespace: my-project
spec:
podSelector: {}
policyTypes:
- Ingress
The oc get services command can be used to determine if a service has been created for the pod that is returning connection refused. If not, the oc expose pod command can be used to create the service.
~]$ oc get services
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
my-service ClusterIP 172.30.166.121 <none> 8080/TCP 3m24s
The oc describe service command can be used to show details about the service. Notice in this example that the service is used to forward requests onto my-pod-zm5g6 on port 8080.
~]$ oc describe service my-service
Name: my-service
Namespace: my-project
Labels: app=my-pod-zm5g6
Annotations: <none>
Selector: deployment=my-pod-zm5g6
Type: LoadBalancer
IP: 172.30.166.121
Port: 8080-tcp 8080/TCP
TargetPort: 8080/TCP
Endpoints: 10.131.5.3:8080
Session Affinity: None
Events: <none>
If there are two (or more pods) in the namespace, the oc exec and curl command can be used to determine if you are able to get a response from the pod with that is returning connection timed out using the service.
~]# oc exec pod/my-pod-vmzmz -- curl my-service:8080 -v
* About to connect() to my-service port 8080 (#0)
* Trying 172.30.166.121...
* Connected to my-service (172.30.166.121) port 8080 (#0)
> Host: my-service:8080
< HTTP/1.1 200
The oc get routes command can be used to list the routes. If not, the oc expose service command can be used to create the route.
~]# oc get routes
NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD
my-route my-route-my-project.apps.openshift.example.com my-service 8080 reencrypt/Redirect None
The curl command can be used to see if you are able to connect using the route.
~]$ curl my-route-my-project.apps.openshift.example.com -v
* TCP_NODELAY set
* connect to 10.84.188.21 failed: Connection refused
* Failed to connect to my-route-my-project.apps.openshift.example.com: Connection refused
* Closing connection 0
curl: (7) Failed to connect to my-route-my-project.apps.openshift.example.com: Connection refused
command terminated with exit code 7
The oc describe route command can be used to display more details about the route. The route should be "exposed" on a router.
~]$ oc describe route my-route
Name: my-route
Namespace: my-project
Created: 17 minutes ago
Labels: name=my-route
Annotations: openshift.io/host.generated=true
Requested Host: my-route-my-project.apps.openshift.example.com
exposed on router default (host router-default.apps.openshift.example.com) 17 minutes ago
Path: /example
TLS Termination: <none>
Insecure Policy: <none>
Endpoint Port: 8080
Service: my-service
Weight: 100 (100%)
Endpoints: 10.217.0.68:8080
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 