
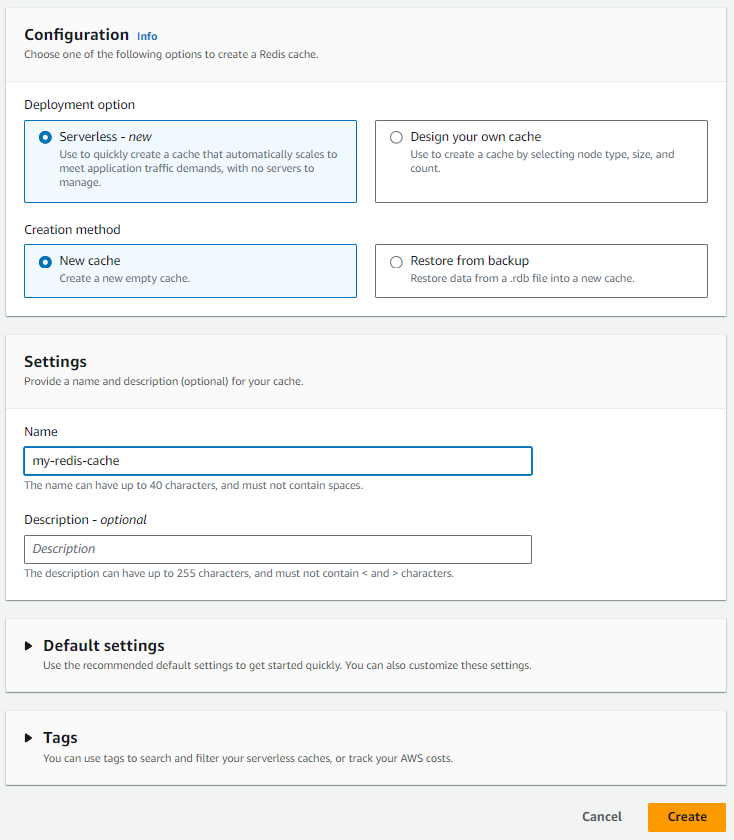
In your Amazon Web Services (AWS) console, go to the ElasticCache page https://console.aws.amazon.com/elasticache and select Get Started > Redis. At a high level, there are two types of Redis you can create.
- serverless (this article)
- dedicated instances
Select Serverless and give your ElastiCache Redis cluster a name and select Create.
I may take a minute or two for the Redis Cluster to be ready. By default, Redis listens for connections on port 6379.
The aws ec2 create-security-group command can be used to create a Security Group in the same Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) as our Redis Cluster.
aws ec2 create-security-group --group-name redis-security-group --description "Redis security group" --vpc-id vpc-0a9d4cb29e2748444
And then the aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress command can be used to allow inbound connections on port 6379.
aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress --group-id sg-abdefg123456789ab --protocol tcp --port 6379 --cidr 0.0.0.0/0
And then Modify your Redis Cluster to be associated with this Security Group.
From your EC2 instance, the openssl s_client connect command can be used to determine if you are able to connect to your Redis cluster on port 6379.
~]$ openssl s_client -connect my-redis-cache-abc123.serverless.use1.cache.amazonaws.com:6379
CONNECTED(00000003)
The redis-cli can be used to see if you can connect to Redis. If you don't have the Redis CLI installed on your EC2 instance in the same Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) as your Redis Cluster, check out my article Install redis-cli from source. It's important to ensure you include BUILD_TLS=yes when making the redis-cli.
make BUILD_TLS=ye
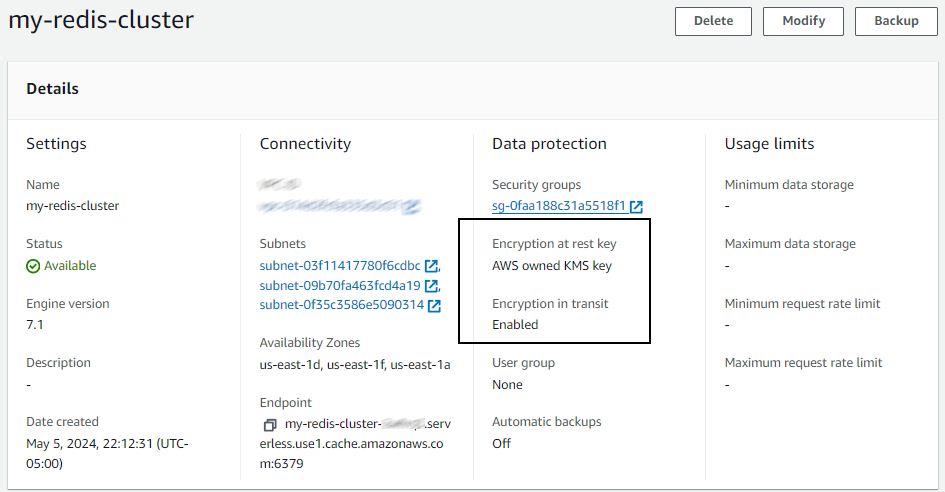
Because by default, AWS Redis Clusters are encrypted with SSL/TLS.
If the connection is successful, you should get an interactive redis command prompt.
~]$ redis-stable/src/redis-cli -c -h my-redis-cache-abc123.serverless.use1.cache.amazonaws.com -p 6379 --tls
my-redis-cache-abc123.serverless.use1.cache.amazonaws.com:6379>
Python can also be used to test the connection to Redis. I would first create a Python3 virtual environment.
python3 -m venv redis
And then activate the Python3 virtual environment.
~]$ source redis/bin/activate
And upgrade pip in the Python3 virtual environment.
/home/ec2-user/redis/bin/python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip
And install the redis module in the Python3 virtual environment.
pip install redis
And here is how you can connect to Redis using Python. This is just the boilerplate code with no error handling.
#!/usr/bin/python3
import redis
client = redis.Redis(
host="my-redis-cluster-abc123.serverless.use1.cache.amazonaws.com",
port=6379,
db=0,
ssl=True)
client.ping()
And here is an example with error handling.
#!/usr/bin/python3
import redis
try:
client = redis.Redis(
host="my-redis-cluster-abc123.serverless.use1.cache.amazonaws.com",
port=6379,
db=0,
ssl=True)
except Exception as exception:
print(f"got the following exception when trying redis.Redis.from_url - {exception}")
else:
print(f"redis.Redis.from_url appears to have been successful")
print(f"client = {client}")
try:
client.ping()
except Exception as exception:
print(f"got the following exception when trying client.ping() - {exception}")
else:
print(f"client.ping() appears to have been successful")
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 