
This assumes:
- You have an ArgoCD server up and running. If not, check out my article Install Red Hat OpenShift GitOps Operator using the console (Argo CD)
- You have installed the ArgoCD CLI.
- You are able to log into ArgoCD using the CLI. If not, check out my article Log into ArgoCD using the CLI on OpenShift
ArgoCD sits between your version control system (such as GitHub) and your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters and is used to create resources (such as deployments, pods, services, routes, config maps and secrets) in a particular namespace in your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters. Almost always, this means you will have YAML files for your various Kubernetes or OpenShift resources in your version control system, such as YAML files for your Kubernetes or OpenShift deployments, YAML files for your Kubernetes or OpenShift secrets, YAML files for your Kubernetes or OpenShift services, et cetera, and ArgoCD will create the corresponding resources in your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters using the YAML files in your version control system. ArgoCD will also ensure the resources on your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters remain in sync with their corresponding YAML files in your version control system.
The argocd app list command can then be used to list the app you have created.
~]$ argocd app list
NAME CLUSTER NAMESPACE PROJECT STATUS HEALTH SYNCPOLICY CONDITIONS REPO PATH TARGET
openshift-gitops/my-app https://kubernetes.default.svc my-project default OutOfSync Healthy Manual SharedResourceWarning(5) https://github.com/my_project/my_repo.git python
openshift-gitops/hello-world https://api.dev.openshift.example.com:6443 default default Manual <none> https://github.com/my_project/my_repo.git python
openshift-gitops/bad-app https://kubernetes.default.svc openshift-gitops default OutOfSync Degraded Manual <none> https://github.com/my_project/my_repo.git resources
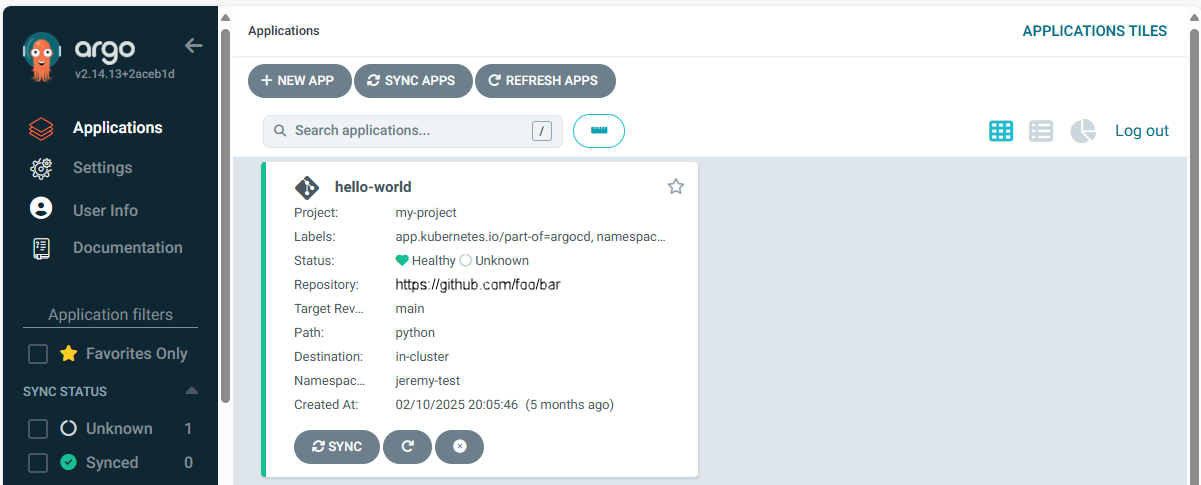
Or in the ArgoCD console at Applications.
Or on the Kubernetes or OpenShift cluster that ArgoCD is in the kubectl (Kubernetes) or oc (OpenShift) exec command can be used to run the argocd cluster list command in the ArgoCD server pod. It is noteworthy that by default the argocd login command will create the hidden .config file in the root directory of the operating system /.config and only root has permission to create files in the root directory of the operating system thus the --config /home/argocd/.config option is used so that the hidden .config file is create in our users home directory.
~]$ SERVER_POD=$(oc get pod --namespace openshift-gitops --selector=app.kubernetes.io/name=openshift-gitops-server --output custom-columns=POD:.metadata.name --no-headers)
~]$ ADMIN_PASSWD=$(oc get secret openshift-gitops-cluster --namespace openshift-gitops --output jsonpath='{.data.admin\.password}' | base64 --decode)
~]$ URL=$(oc get routes --namespace openshift-gitops --selector=app.kubernetes.io/name=openshift-gitops-server --output jsonpath="{.items[*].spec.host}")
~]$ oc exec $SERVER_POD --namespace openshift-gitops -- /bin/bash -c "argocd login --username admin --password $ADMIN_PASSWD $URL:443 --insecure --grpc-web --config /home/argocd/.config; argocd app list --server $URL:443 --insecure --grpc-web --config /home/argocd/.config"
'admin:login' logged in successfully
NAME CLUSTER NAMESPACE PROJECT STATUS HEALTH SYNCPOLICY CONDITIONS REPO PATH TARGET
openshift-gitops/my-app https://kubernetes.default.svc my-project default OutOfSync Healthy Manual SharedResourceWarning(5) https://github.com/my_project/my_repo.git python
openshift-gitops/hello-world https://api.dev.openshift.example.com:6443 default default Manual <none> https://github.com/my_project/my_repo.git python
openshift-gitops/bad-app https://kubernetes.default.svc openshift-gitops default OutOfSync Degraded Manual <none> https://github.com/my_project/my_repo.git resources
The kubectl (Kubernetes) or oc (OpenShift) login command to log into the Kubernetes or OpenShift cluster that ArgoCD is running in and then use the auth can-i command can be used to determine if you have permission to list an ArgoCD application.
~]$ oc login -u john.doe api.dev.openshift.example.com:6443
~]$ oc auth can-i list applications.argoproj.io
yes
Assuming you have permission to list an application the kubectl (Kubernetes) or oc (OpenShift) get applications.argoproj.io command can be used to list the ArgoCD applications.
~]$ oc get applications.argoproj.io --namespace <the namespace argocd is in, usually argocd or openshift-gitops>
NAME SYNC STATUS HEALTH STATUS
my-app Synced Healthy
hello-world
bad-app OutOfSync Degraded
The argocd app get command can be used to display more details.
~]$ argocd app get openshift-gitops/my-app
Name: openshift-gitops/my-app
Project: default
Server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
Namespace: my-project
URL: https://openshift-gitops-server-openshift-gitops.apps.openshift.example.com/applications/my-app
Source:
- Repo: https://github.com/my_project/my_repo.git
Target:
Path: python
SyncWindow: Sync Allowed
Sync Policy: Manual
Sync Status: OutOfSync from (dbc57d6)
Health Status: Missing
GROUP KIND NAMESPACE NAME STATUS HEALTH HOOK MESSAGE
apps Deployment my-project python OutOfSync Missing
The --output json flag can be used to display output as JSON instead of YAML.
~]$ argocd app get openshift-gitops/my-app --output json
{
"metadata": {
"name": "my-app",
"namespace": "openshift-gitops",
"uid": "e6d7b10c-74f0-4c2a-b4b2-6d82a8b987ca",
"resourceVersion": "405164309",
"generation": 2,
"creationTimestamp": "2024-12-20T02:34:18Z",
"managedFields": [
{
"manager": "argocd-application-controller",
"operation": "Update",
"apiVersion": "argoproj.io/v1alpha1",
"time": "2024-12-20T02:34:18Z",
"fieldsType": "FieldsV1",
"fieldsV1": {
"f:status": {
"f:controllerNamespace": {},
"f:health": {
"f:status": {}
},
"f:reconciledAt": {},
"f:resources": {},
"f:sourceType": {},
"f:sync": {
"f:comparedTo": {
"f:destination": {
"f:namespace": {},
"f:server": {}
},
"f:source": {
"f:path": {},
"f:repoURL": {}
}
},
"f:revision": {},
"f:status": {}
}
}
}
},
{
"manager": "argocd-server",
"operation": "Update",
"apiVersion": "argoproj.io/v1alpha1",
"time": "2024-12-20T02:34:18Z",
"fieldsType": "FieldsV1",
"fieldsV1": {
"f:spec": {
".": {},
"f:destination": {
".": {},
"f:namespace": {},
"f:server": {}
},
"f:project": {},
"f:source": {
".": {},
"f:path": {},
"f:repoURL": {}
}
},
"f:status": {
".": {},
"f:health": {},
"f:summary": {},
"f:sync": {
".": {},
"f:comparedTo": {
".": {},
"f:destination": {},
"f:source": {}
}
}
}
}
}
]
},
"spec": {
"source": {
"repoURL": "https://github.com/my_project/my_repo.git",
"path": "python"
},
"destination": {
"server": "https://kubernetes.default.svc",
"namespace": "my-project"
},
"project": "default"
},
"status": {
"resources": [
{
"group": "apps",
"version": "v1",
"kind": "Deployment",
"namespace": "my-project",
"name": "python",
"status": "OutOfSync",
"health": {
"status": "Missing"
}
}
],
"sync": {
"status": "OutOfSync",
"comparedTo": {
"source": {
"repoURL": "https://github.com/my_project/my_repo.git",
"path": "python"
},
"destination": {
"server": "https://kubernetes.default.svc",
"namespace": "my-project"
}
},
"revision": "dbc57d62045ddae6c68f925b7cb3f6a1f621bd81"
},
"health": {
"status": "Missing"
},
"reconciledAt": "2024-12-20T02:34:18Z",
"sourceType": "Directory",
"summary": {},
"controllerNamespace": "openshift-gitops"
}
}
Manifest Files
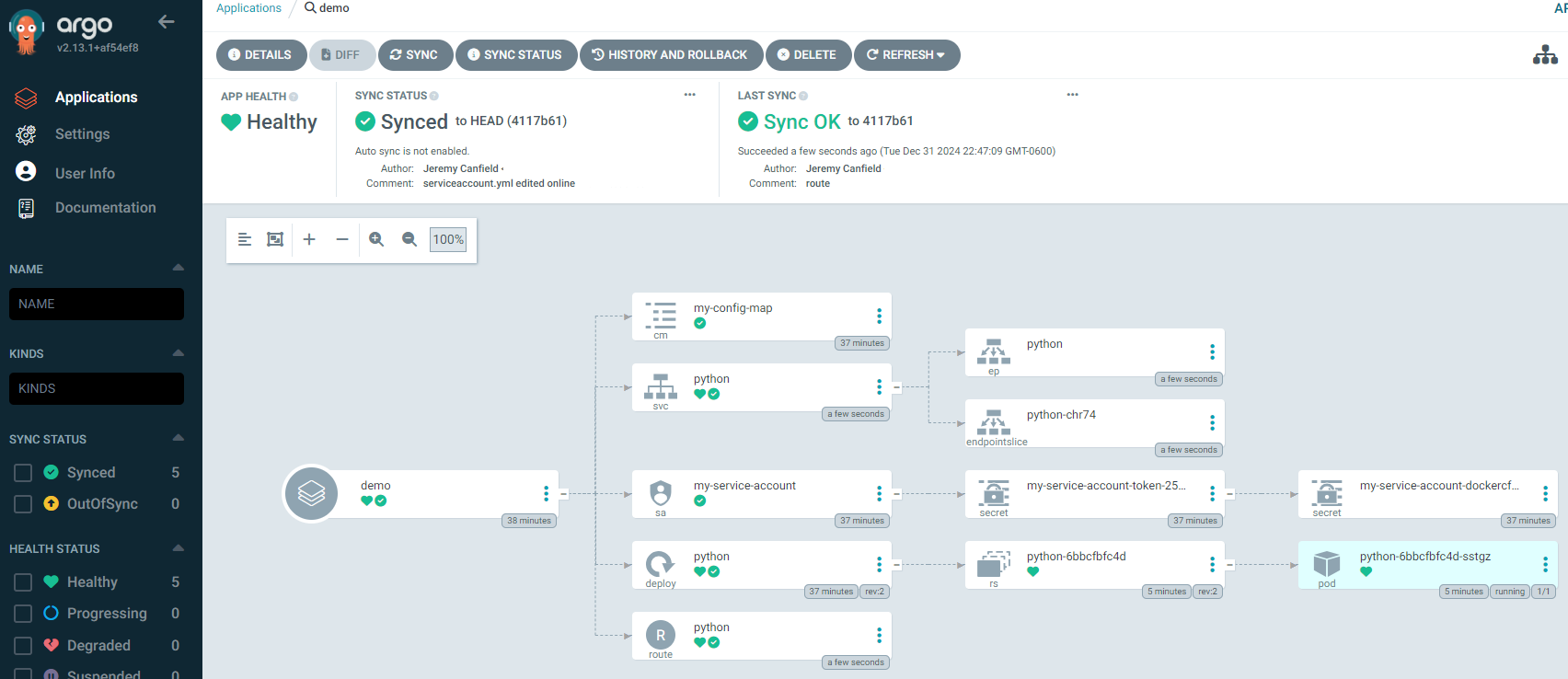
An ArgoCD app contains one or more resources (such as deployments, pods, services, routes, config maps and secrets) for a particular namespace in your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters. In this example, the "demo" app contains a config map (cm), a service (svc), a service account (sa), a deployment (deploy), a route, an endpoint (ep), an endpoint slice, secrets, a replia set (rs), and a pod. When the app is created in ArgoCD, ArgoCD creates manifest files for each resources. For example, if the app contains a deployment, this means there was a YAML file for the deployment in the version control system (such as GitHub) being used by the app in ArgoCD. When the app was created in ArgoCD, ArgoCD would have fetched the deployment YAML file from the version control system and created a manifest file in ArgoCD for the deployment. The manifest file in ArgoCD is similar (but not identical) to the YAML file from the version control system.
At certain intervals, typically once every 3 minutes, ArgoCD will refresh to compare the manifest file in ArgoCD to the corresponding file in the version control system and if any differences are detected, ArgoCD will update it's manifest file to match the corresponding file in the version control system and ArgoCD will then attempt a sync to update the resource in your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters. Assuming this works as designed, it's an excellent way to update resources on your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters. You simply updated the YAML file in your version control system, then ArgoCD takes care of updating the resource on your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters.
Almost always, after creating an app, you can simply wait a few minutes for the application to sync or you can manually sync.
In the ArgoCD console, you should see something like this, showing the various resources in your namespace.
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 