
ArgoCD sits between your version control system (such as GitHub) and your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters and is used to create resources (such as deployments, pods, services, routes, config maps and secrets) in a particular namespace in your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters. Almost always, this means you will have YAML files for your various Kubernetes or OpenShift resources in your version control system, such as YAML files for your Kubernetes or OpenShift deployments, YAML files for your Kubernetes or OpenShift secrets, YAML files for your Kubernetes or OpenShift services, et cetera, and ArgoCD will create the corresponding resources in your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters using the YAML files in your version control system. ArgoCD will also ensure the resources on your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters remain in sync with their corresponding YAML files in your version control system.
Manifest Files
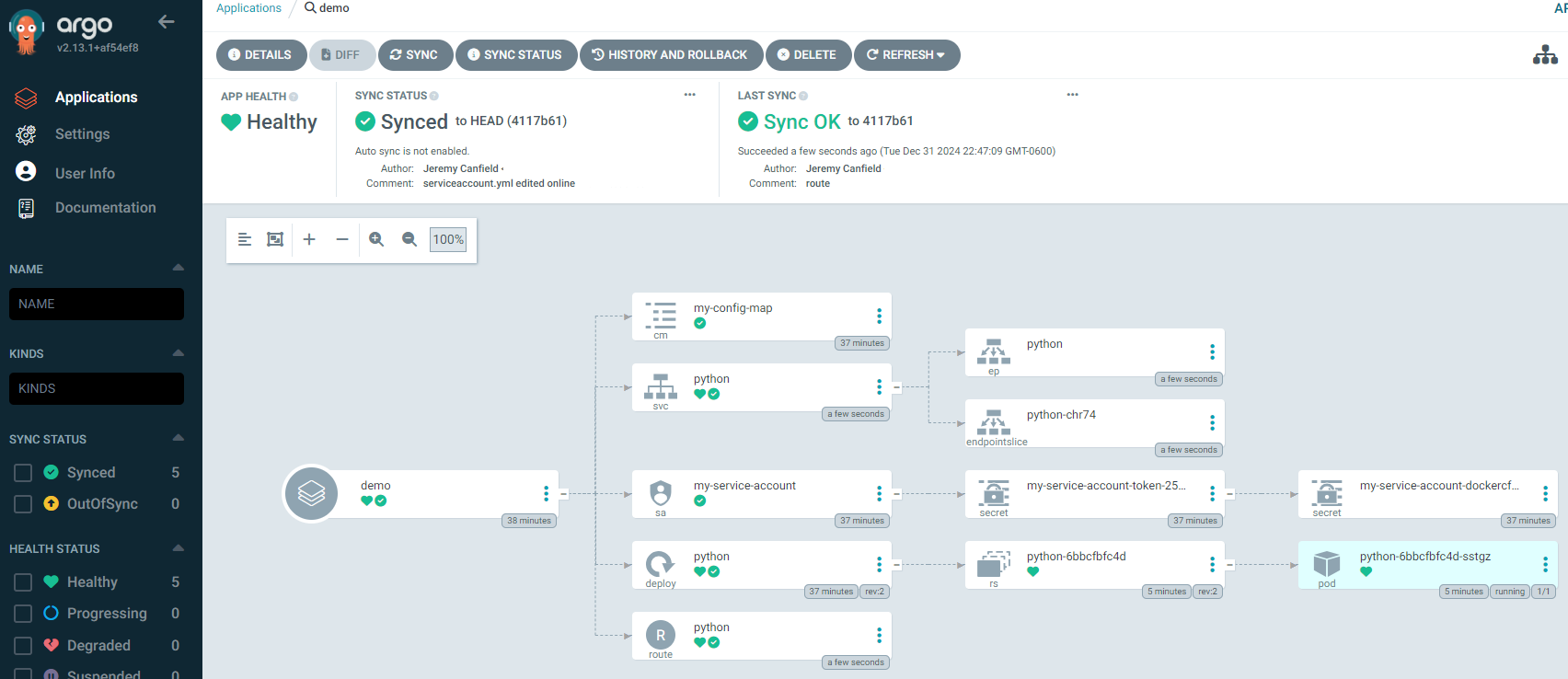
An ArgoCD app contains one or more resources (such as deployments, pods, services, routes, config maps and secrets) for a particular namespace in your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters. In this example, the "demo" app contains a config map (cm), a service (svc), a service account (sa), a deployment (deploy), a route, an endpoint (ep), an endpoint slice, secrets, a replia set (rs), and a pod. When the app is created in ArgoCD, ArgoCD creates manifest files for each resources. For example, if the app contains a deployment, this means there was a YAML file for the deployment in the version control system (such as GitHub) being used by the app in ArgoCD. When the app was created in ArgoCD, ArgoCD would have fetched the deployment YAML file from the version control system and created a manifest file in ArgoCD for the deployment. The manifest file in ArgoCD is similar (but not identical) to the YAML file from the version control system.
At certain intervals, typically once every 3 minutes, ArgoCD will refresh to compare the manifest file in ArgoCD to the corresponding file in the version control system and if any differences are detected, ArgoCD will update it's manifest file to match the corresponding file in the version control system and ArgoCD will then attempt a sync to update the resource in your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters. Assuming this works as designed, it's an excellent way to update resources on your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters. You simply updated the YAML file in your version control system, then ArgoCD takes care of updating the resource on your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters.
In the ArgoCD console, you should see something like this, showing the various resources in your namespace.
This assumes:
- You have an ArgoCD server up and running. If not, check out my article Install Red Hat OpenShift GitOps Operator using the console (Argo CD)
- You have installed the ArgoCD CLI.
- You are able to log into ArgoCD using the CLI. If not, check out my article Log into ArgoCD using the CLI on OpenShift
The argocd app list command can be used to list the app you have created.
~]$ argocd app list
NAME CLUSTER NAMESPACE PROJECT STATUS HEALTH SYNCPOLICY CONDITIONS REPO PATH TARGET
openshift-gitops/demo https://kubernetes.default.svc default default OutOfSync Missing Manual <none> https://github.com/my_project/my_repo.git python
And then the argocd app manifest <app name> command can be used to display the manifests for the application.
~]$ argocd app manifests demo
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/instance: demo
name: my-service-account
namespace: my_project
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 