
This assumes:
- You have an ArgoCD server up and running. If not, check out my article Install Red Hat OpenShift GitOps Operator using the console (Argo CD)
- You have installed the ArgoCD CLI.
- You are able to log into ArgoCD using the CLI. If not, check out my article Log into ArgoCD using the CLI on OpenShift
ArgoCD sits between your version control system (such as GitHub) and your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters and is used to create resources (such as deployments, pods, services, routes, config maps and secrets) in a particular namespace in your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters. Almost always, this means you will have YAML files for your various Kubernetes or OpenShift resources in your version control system, such as YAML files for your Kubernetes or OpenShift deployments, YAML files for your Kubernetes or OpenShift secrets, YAML files for your Kubernetes or OpenShift services, et cetera, and ArgoCD will create the corresponding resources in your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters using the YAML files in your version control system. ArgoCD will also ensure the resources on your Kubernetes or OpenShift clusters remain in sync with their corresponding YAML files in your version control system.
The argocd repo list command can be used to list the repo's you have added to ArgoCD.
~]$ argocd repo list
TYPE NAME REPO INSECURE OCI LFS CREDS STATUS MESSAGE PROJECT
git foo-bar https://github.com/foo/bar.git false false false false Successful default
Assuming the repo you want to add has not already been added to ArgoCD, the argocd repo add command can be used to add the repo to ArgoCD. If the repo is a public repo, you should be able to add the repo without having to provide any sort of authentication, such as a username and password.
argocd repo add https://github.com/foo/bar.git
Or in the ArgoCD console at Settings > Repositories > Connect Repo.
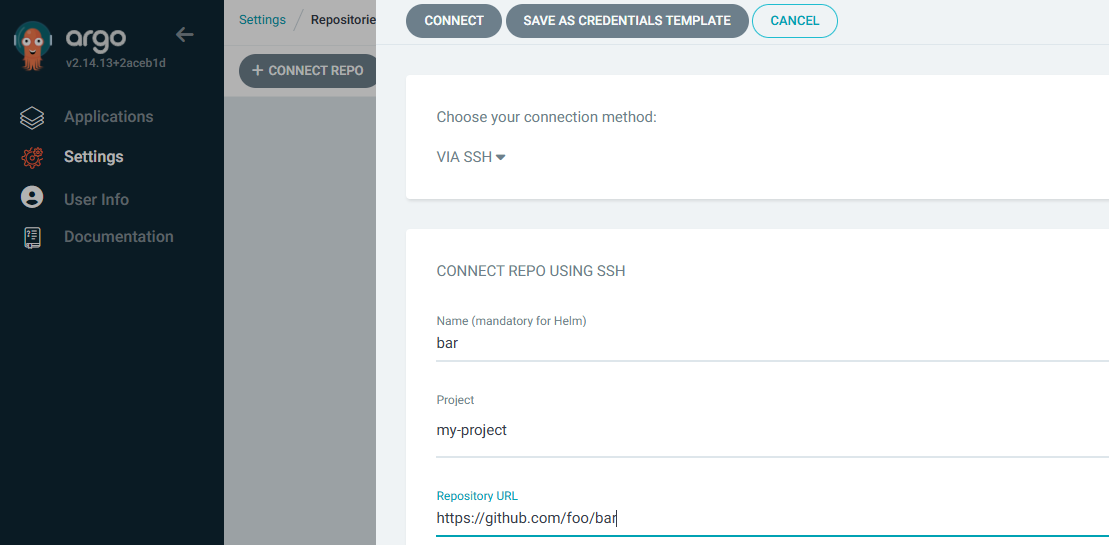
For private repos, you need to authenticate. If using the HTTPS URL for the private repo, it's pretty common to provide a username and password.
argocd repo add https://github.com/foo/bar.git --username john.doe --password itsasecret
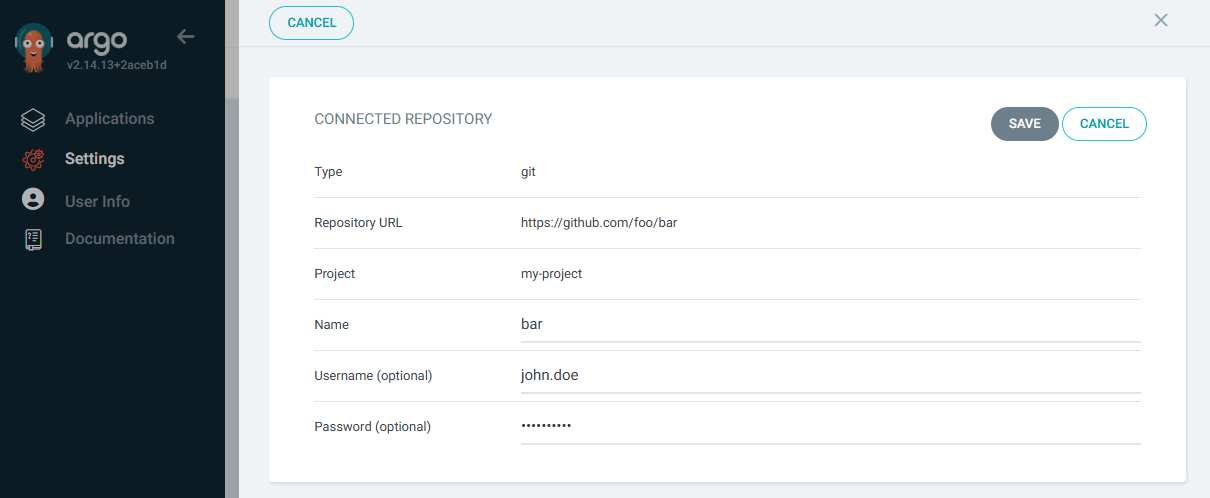
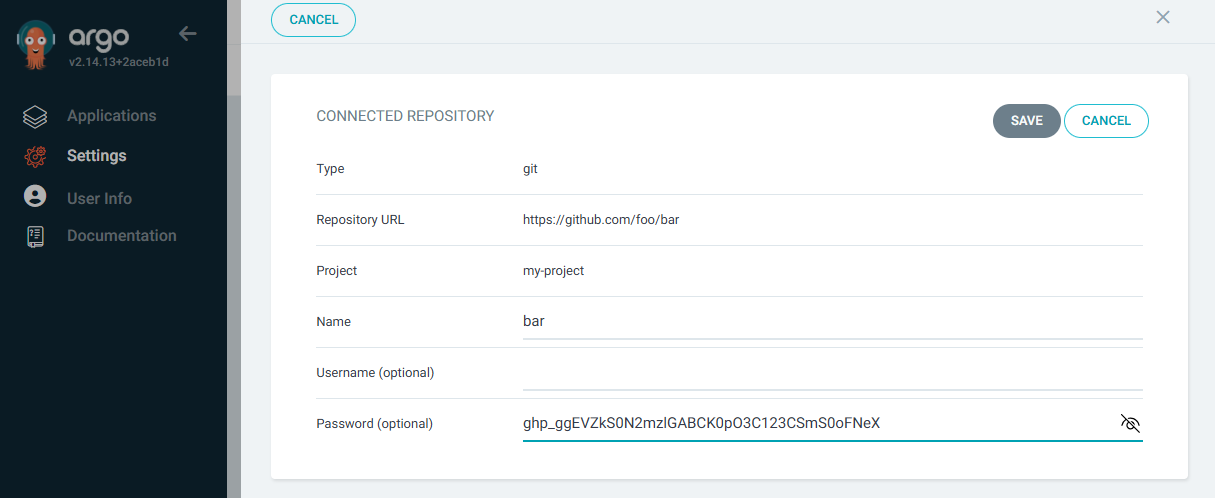
If adding the repo using the console, at Settings > Repositories > Connect Repo there is no option to provide a username and password, which is totally weird. However, you can go ahead and add the repo without including the username and password. Then at Settings > Repositories, select the repo and the panel that appears has an Edit button that allows you to provide the username and password.
Or you can use an Access Token, such as a GitHub Personal Access Token (PAT).
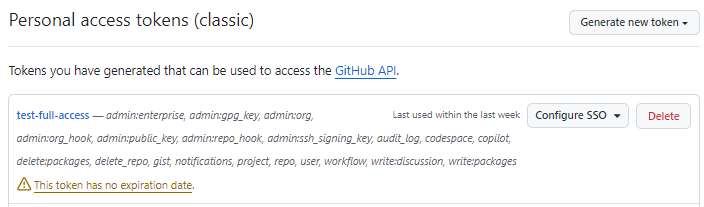
When using an Access Token, the username must be a non empty string such as a single whitespace and password will be the Access Token.
argocd repo add https://github.com/foo/bar.git --username ' ' --password 'ghp_ggEVZkS0N2mzlGABCK0pO3C123CSmS0oFNeX'
If adding the repo using the console, at Settings > Repositories > Connect Repo there is no option to provide a username and password, which is totally weird. However, you can go ahead and add the repo without including the username and password. Then at Settings > Repositories, select the repo and the panel that appears has an Edit button that allows you to provide the username and password. Since username must be a non-empty string, you will need to click on the username field and press the spacebar once so that the username contains a single whitespace. Yep, that's counter intuitive. Hopefully the ArgoCD folks eventually address this.
To add a repo using SSH, you will use an SSH private key. ArgoCD version 2.4 uses OpenSSH version 8.9. OpenSSH version 8.8 dropped support for ssh-rsa. The argocd --version command can be used to display the version of ArgoCD you are using.
~]$ argocd version
argocd: v2.13.2+dc43124
If you are using ArgoCD version 2.4 or higher, you must not create an RSA key. Instead, you will almost always go with an ed25519 SSH public/private keypair.
You may also need to ensure that the SSH key is an OpenSSH private key and has comment argocd (check out this article for more details on this). The ssh-keygen command can be used to create the OpenSSH public/private keypair.
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -N '' -C argocd -f $HOME/.ssh/argocd
In this scenario, you would also need to add the SSH key in your GitHub account.
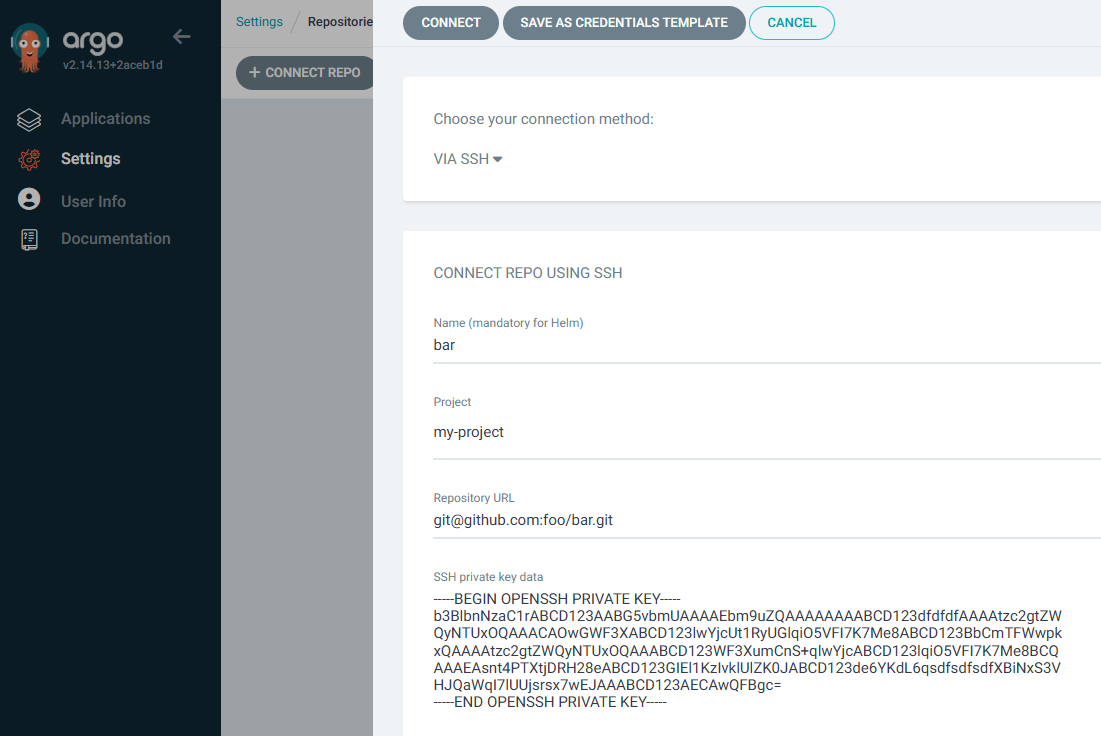
And then you can add the repo using the SSH private key.
argocd repo add git@github.com:foo/bar.git --ssh-private-key-path $HOME/.ssh/argocd
Or in the ArgoCD console at Settings > Repositories > Connect Repo.
Or you can create a YAML file that will be used to create a Kubernetes or OpenShift secret. The secret will add the repo to ArgoCD. For example, here is what you could have in your YAML file to add a GitHub repo to ArgoCD using an SSH key for the authentication to the GitHub repo.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
annotations:
managed-by: argocd.argoproj.io
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type: repository
name: my-repo
namespace: openshift-gitops
type: Opaque
stringData:
name: my-repo
project: my-project
type: git
url: https://github.com/foo/bar.git
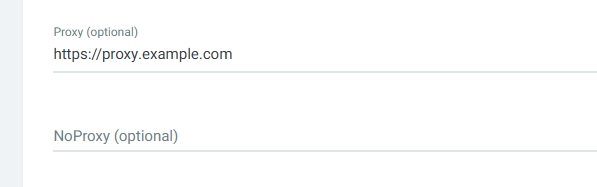
proxy: https://proxy.example.com # optional
sshPrivateKey: |
-----BEGIN OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----
MIIJK.....xdi3fPx
-----END OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----
And then the kubectl (Kubernetes) or oc (OpenShift) apply command can be used to create a secret from a YAML file.
~]$ oc apply -f repo.yml
secret/my-repo created
It's pretty common to give the repo a name and to map the repo to an ArgoCD project.
argocd repo add git@github.com:foo/bar.git \
--ssh-private-key-path ~/.ssh/id_rsa \
--name my-repo \
--project default
If you want ArgoCD to use a proxy to connect to the repo the --proxy option can be used.
argocd repo add git@github.com:foo/bar.git \
--ssh-private-key-path ~/.ssh/id_rsa \
--name my-repo \
--project default \
--proxy https://proxy.example.com
Or in the ArgoCD console at Settings > Repositories > Connect Repo and entry the http or https proxy URL.
Assuming the repo has been successfully created in ArgoCD, the argocd repo list command should include the repo you added.
~]$ argocd repo list
TYPE NAME REPO INSECURE OCI LFS CREDS STATUS MESSAGE PROJECT
git foo-bar https://github.com/foo/bar.git false false false false Successful default
git my-repo https://github.com/acme/my-repo.git false false false false Successful default
Likewise, the kubectl (Kubernetes) or oc (OpenShift) get secrets command can be used to list the secrets that in the namespace ArgoCD is running in.
~]# oc get secrets --namespace openshift-gitops
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
repo-2979096065 Opaque 4 17m
The --output yaml option can be used to display the YAML of the secret.
~]$ oc get secret repo-2979096065 --namespace openshift-gitops --output yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
name: YmFy
project: bXktcHJvamVjdA==
type: Z2l0
url: aHR0cHM6Ly9naXRodWIuY29tL2Zvby9iYXI=
kind: Secret
metadata:
annotations:
managed-by: argocd.argoproj.io
creationTimestamp: "2025-07-09T01:38:32Z"
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type: repository
name: repo-2979096065
namespace: openshift-gitops
resourceVersion: "571713113"
uid: 97eeccbe-d2c0-4248-b593-a3d2c972b414
type: Opaque
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 