
A Docker image contains the code used to create a Docker container, such as creating a Nginx web server, or a mySQL server, or a home grown app, and the list goes on. In this way, an image is like a template used to create a container. An image is kind of like a virtual machine, but much more light weight, using significantly less storage a memory (containers are usually megabytes in size).
Let's create the following files and directories.
├── Dockerfile
├── requirements.txt
├── app (directory)
│ ├── main.py
│ ├── __init__.py
Dockerfile will have something like this.
FROM python:latest
WORKDIR /code
COPY ./requirements.txt /code/requirements.txt
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade -r /code/requirements.txt
requirements.txt will need the fastapi and fastapi-cli packages.
fastapi==0.115.6
fastapi-cli==0.0.7
Let's say main.py has the following, the boilerplate code needed to run a FastAPI app.
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
def home():
return {"Hello": "World"}
__init__.py will be an empty file.
Then use the docker build command to create the image, running this command in the same directory as the Dockerfile.
docker build --tag demo:latest .
The docker images command can be used to display the image.
~]$ sudo docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
demo latest 60b476e79885 5 days ago 968MB
The following command can then be used to create and start the container. Let's break down this command.
- The docker run command is used to create and start the container.
- The --detach flag is used to run the container in the background.
- The --publish option is used both the Docker server listens on port 12345 and the container listens on port 80
- The --volume option is used to mount the main.py and __init__.py files on your Docker system to the /app directory in the container.
- The --name option is used to give the container a specific name.
- The --restart unless-stopped option is used so that the container is started if the Docker server is restarted
- The demo:latest image is used
- The fastapi run /app/main.py command is run in the container to run main.py
sudo docker run \
--detach \
--restart unless-stopped \
--publish 0.0.0.0:12345:80 \
--volume /path/to/app/main.py:/app/main.py \
--volume /path/to/app/__init__.py:/app/__init__.py \
--name fastapi \
demo:latest \
fastapi run /app/main.py
The docker container ls command can be used to ensure the container is running.
~]$ sudo docker container ls -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
b751ea01885b demo:latest "fastapi run /app/ma…" 8 minutes ago Up 8 minutes 0.0.0.0:12345->8000/tcp fastapi
The docker logs command should return something like this.
~]$ sudo docker logs fastapi
FastAPI Starting production server 🚀
Searching for package file structure from directories with
__init__.py files
Importing from /
module 📁 app
├── 🐍 __init__.py
└── 🐍 main.py
code Importing the FastAPI app object from the module with the following
code:
from app.main import app
app Using import string: app.main:app
server Server started at http://0.0.0.0:8000
server Documentation at http://0.0.0.0:8000/docs
Logs:
INFO Started server process [1]
INFO Waiting for application startup.
INFO Application startup complete.
INFO Uvicorn running on http://0.0.0.0:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
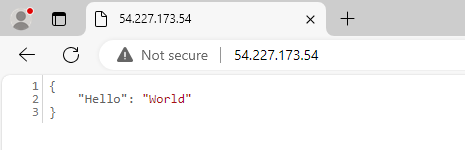
curl can be used to submit a GET request which should return Hello World. It works!
~]$ curl localhost:12345/
{"Hello": "World"}
If running Docker on a Linux system, ensure connections are allowed in firewalld or iptables on ports 80 and 443.
firewall-cmd --add-service=http --permanent
firewall-cmd --add-service=https --permanent
firewall-cmd --reload
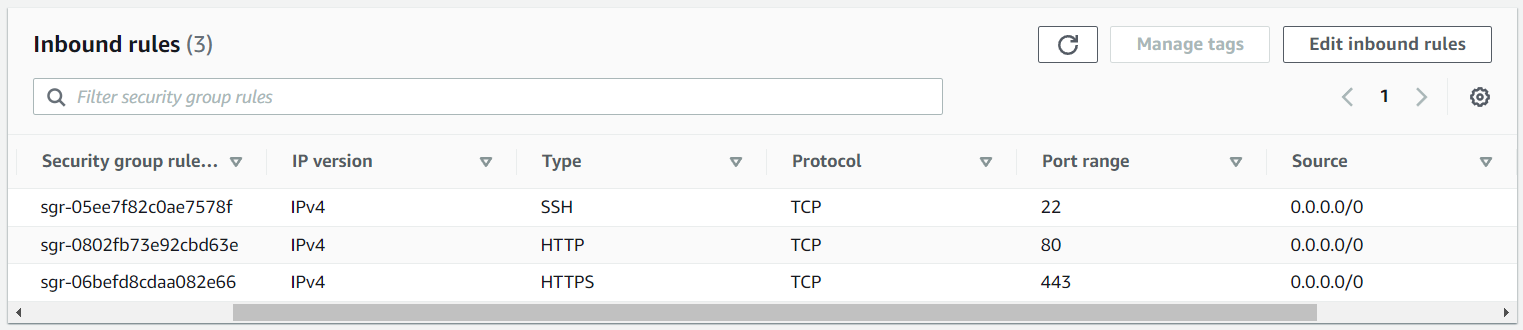
If running Docker on an Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2 Instance, ensure the Security Group Inbound Rules allow connections on ports 80 and 443.
You should then be able to go to the hostname or IP address of your Docker system and FastAPI should return a response.
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 