
Egress provides a way for an application deployed on OpenShift to send traffic out of the OpenShift cluster. For example, an application in a pod running on OpenShift may want to send a request to https://api.example.com and get a response from api.example.com.
There are two common types of Container Network Interfaces (CNI) used by OpenShift
- OpenShiftSDN
- OVNKubernetes
The following command can be used to determine if your OpenShift cluster is using OpenShiftSDN or OVNKubernetes.
oc get network.config/cluster --output jsonpath="{.spec.networkType}"
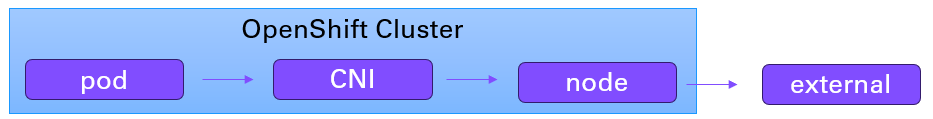
It is noteworthy that you may not need to assign an EgressIP address to your OpenShfit namespace to be able to send a request to a URL outside of your OpenShift cluster. The most basic architecture is that the OpenShift Container Network Interface (CNI) (OpenShiftSDN or OVNKubernetes) will translate the pod IP address to the external IP address of the node that the pod is running on. Assuming there is no additional IP or network address translation, when the request reaches the external URL, the request will show as coming from the nodes external IP address.
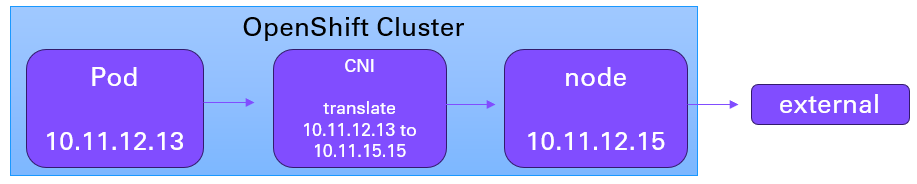
For example, let's say the pod IP address is 10.11.12.13 and the pod is running on my-node.
~]$ oc get pods --output wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE
my-pod 1/1 Running 0 91d 10.11.12.13 my-node
And let's say the nodes external IP address is 10.11.12.15.
~]$ oc get node my-node --output wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP
my-nodek Ready compute,worker 215d v1.31.11 10.11.12.14 10.11.12.15
In this scenario, the OpenShift Container Network Interface (CNI) (OpenShiftSDN or OVNKubernetes) will translate the pod IP address 10.11.12.13 to the node external IP address 10.11.12.15. Assuming there is no additional IP or network address translation, when the request reaches the external URL, the request will show as coming from the nodes external IP address 10.11.12.15.
Optionally, an Egress Network Policy is like a firewall with a list of allow and deny rules, to allow or deny requests to certain DNS hostnames and/or IP addresses, as an additional layer of security. This is often used as a sort of zero trust policy, to deny all Egress traffic except for requests that are explicitly allowed.
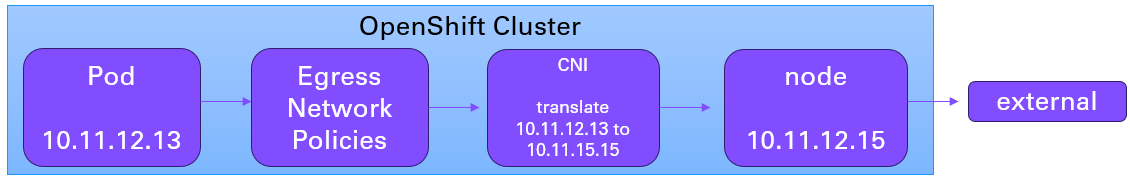
One reason you may want to assign an EgressIP address to a namespace is to be to review the Container Network Interface (CNI) logs and to know what namespace a request is coming from based on the EgressIP address.
- If your OpenShift cluster is using OpenShiftSDN, then NetNamespace is used to assign an egress IP address to one or more namespaces.
- If your OpenShift cluster is using OVNKubernetes, then EgressIP (this article) is used to assign an egress IP address to one or more namespaces.
Let's say you have the following YAML file. This will create the egressip resource mapping IP address 10.11.12.13 to namespace my-project.
apiVersion: k8s.ovn.org/v1
kind: EgressIP
metadata:
name: my-project
spec:
egressIPs:
- 10.11.12.13
namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/metadata.name: my-project
The oc apply command can be used to create the egressip resource.
oc apply --filename egress.yml
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 