Docker - Mount a file or directory in a container using the docker run -m or --mount command


by
Jeremy Canfield |
Updated: November 25 2025
| Docker articles
The --mount or --volume option can be used to:
- mount a file or directory on your Docker system to a file or directory in the container
- mount an NFS share in the container
You can use:
- the -m or --mount option (this article)
- the -v or --volume option
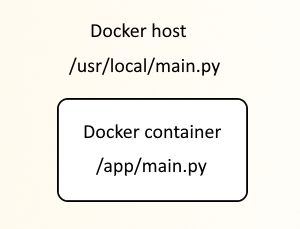
For example, let's can use the --mount or --volume option to mount /usr/local/main.py on the Docker host system to /app/main.py in a Docker container.

For example, here is how you could mount /usr/local/main.py on the Docker system to /app/main.py in the container.
sudo docker run \
--mount \
src=/usr/local/main.py,\
dst=/app/main.py,\
type=bind \
foo:latest
As an example, let's say you have a container named foo, and you want to mount an NFS share in the container. In this example, the the docker run command is used to start/create the container using the foo:latest image.
sudo docker run \
--mount \
src=mynfsshare,\
dst=/mnt,\
type=volume,\
volume-driver=local,\
volume-opt=type=nfs,\
volume-opt=device=:/,\
\"volume-opt=o=addr=10.11.12.13,nfsvers=4.1,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576,hard,timeo=600,retrans=2,noresvport\"\
foo:latest
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 