
A certificate can be used to encrypt the resources being transmitted to clients. In this example, a dedicated certificate will be placed on the Nginx web server so that HTTPS can be used.
A certificate from a trusted CA (certificate authority), such as www.verisign.com, or using a self signed certificate can be used. The main difference between a certificate from a trusted CA and a self signed certificate is that web browsers will display a warning message when a self signed certificate is used. OpenSSL can be used to create the self signed public certificate and private key.
AVOID TROUBLE
The certificate Common Name (CN) will almost always need to match the DNS hostname of the web server the certificate is being used for. For example, if the certificate will be used for SSL / HTTPS on the web server producing www.freekb.net, then the certificates common name (CN) will need to be www.freekb.net or *.freekb.net.
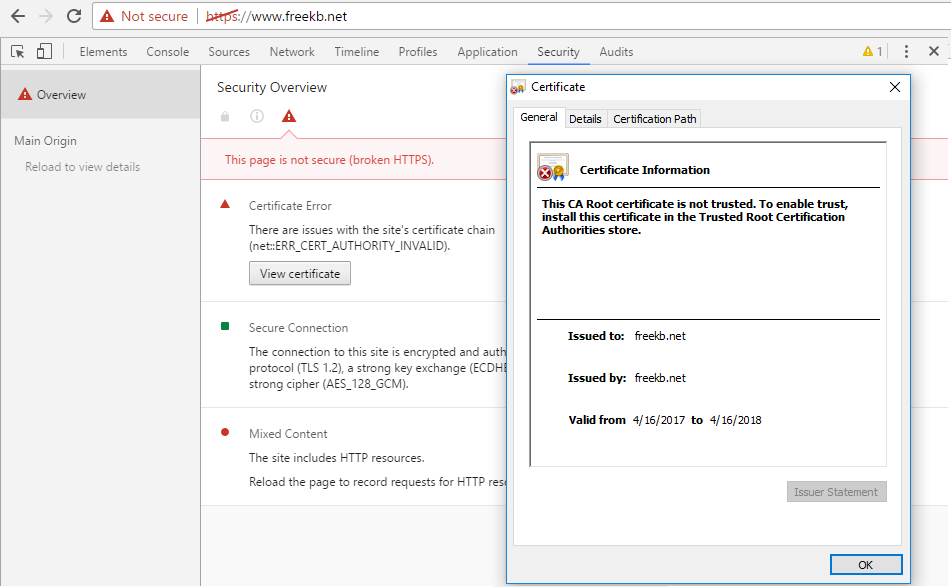
In this example, a self signed public certificate was created for freekb.net, and Chrome compalins that the root certificate is not trusted, because the certificate is not in the trusted root certificate authorities store. This is the expected behavior of a self signed certificate.
Inside of the server block in the /etc/nginx/nginx.conf file, add the following. Replace www.example.com with your domain name.
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name www.example.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/pki/tls/certs/www.example.com.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/pki/tls/private/www.example.com.key;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
}
In the prior markup, ssl_protocols is set to TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2. As long as the browser is configured to use TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, or TLS 1.2, the connection will be allowed.

In the prior markup, ssl_ciphers is set to High and not Null and not MD5. If you would rather specify the ciphers being used, you can use one or more of the following ciphers. Navigate to https://cc.dcsec.uni-hannover.de to determine the cipher's supported by the browser.
EECDH+ECDSA+AESGCM
EECDH+aRSA+AESGCM
EECDH+ECDSA+SHA384
EECDH+ECDSA+SHA256
EECDH+aRSA+SHA384
EECDH+aRSA+SHA256
EECDH+aRSA+RC4
EECDH
EDH+aRSA
RC4
The ps command can be used to determine if your system is using init or systemd. If PID 1 is init, then you will use the service command. If PID 1 is systemd, then you will use the systemctl command.
If your system is using systemd, use the systemctl command to restart nginx.
systemctl restart nginx
If your system is using init, use the service command to restart nginx.
service nginx restart
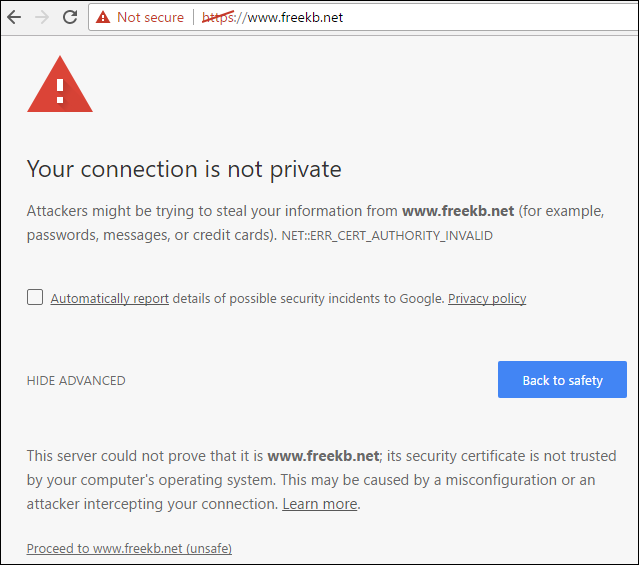
Ensure iptables is configured to allow traffic on port 443. You should now be able to navigate to your site using https. The browser will complain that the site is not trusted. This is normal when using a self-signed certificated. You can proceed to the site.
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 