
Let's say there is a WebSphere data source that has a JNDI of jdbc/mySQL.
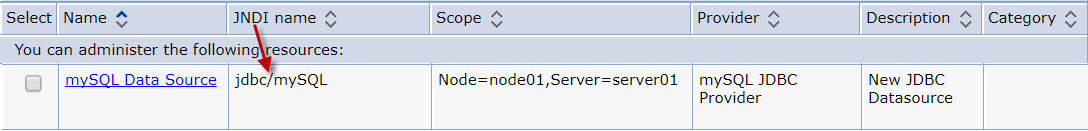
In this scenario, you would add the following to WEB-INF/web.xml.
<resource-ref>
<res-ref-name>jdbc/mySQL</res-ref-name>
<res-type>javax.sql.DataSource</res-type>
<res-auth>Container</res-auth>
</resource-ref>
J2C authentication alias
see IBM WebSphere - JDBC data source and J2C alias
SQL query
Here is an example of a JSP page that makes a connection to the database associated with jdbc/mySQL.
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/sql" prefix="sql" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<sql:query var="myvar" dataSource="jdbc/mySQL">
select * from foo;
</sql:query>
Now, if you manually deploy the application, there will be a prompt where you will map the data source to JNDI jdbc/mySQL.
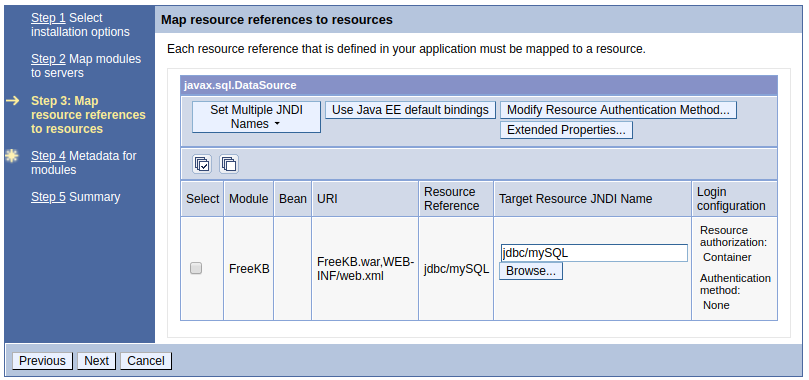
A much better option is to place the ibm-web-bnd.xml file in the WEB-INF folder of your WAR to define the JNDI. If you do this, you will not be prompted to define the JNDI when manually deploying an app to WebSphere. Instead, the application will use the data source defined in ibm-web-bnd.xml.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-bnd
xmlns="http://websphere.ibm.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://websphere.ibm.com/xml/ns/javaee http://websphere.ibm.com/xml/ns/javaee/ibm-web-bnd_1_0.xsd"
version="1.0">
<resource-ref name="jdbc/mySQL" binding-name="jdbc/mySQL" />
</web-bnd>
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 