
Let's say you've created a self signed certificate using OpenSSL. Notice in this example that the common name (CN) of the public certificate is mail.example.com. More on this in a moment . . . read on.
openssl req -x509 -sha512 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout example.key -out mail.example.com.cer -subj "/C=US/ST=California/L=Los Angeles/O=Acme/OU=IT/CN=mail.example.com"
Typically, you'll want to public certificate and private key to have the following permissions.
chmod 0400 example.key
chmod 0644 mail.example.com.cer
The openssl x509 command can be used to show the details of the self signed certificate. Notice the CN is mail.example.com.
~]# openssl x509 -in mail.example.com.cer -text -noout
Certificate:
Data:
Version: 1 (0x0)
Serial Number: 12403619368338344086 (0xac2282192af64896)
Signature Algorithm: sha512WithRSAEncryption
Issuer: C=US, ST=California, L=Los Angeles, O=Acme, OU=IT, CN=mail.example.com
Validity
Not Before: Sep 5 12:13:43 2022 GMT
Not After : Sep 5 12:13:43 2023 GMT
Subject: C=US, ST=California, L=Los Angeles, O=Acme, OU=IT, CN=mail.example.com
Add the following to the /etc/postfix/main.cf file, using the private key (example.key) and public certificate (mail.example.com.cer) files you just created.
smtpd_tls_security_level = encrypt
smtpd_tls_auth_only = yes
smtpd_tls_key_file = /usr/local/certificates/example.key
smtpd_tls_cert_file = /usr/local/certificates/mail.example.com.cer
smtpd_tls_loglevel = 1
smtpd_tls_session_cache_timeout = 3600s
smtpd_tls_session_cache_database = btree:/var/lib/postfix/
smtpd_tls_cachetls_random_source = dev:/dev/urandom
tls_random_exchange_name = /var/lib/postfix/prng_exch
- smtpd_tls_security_level: Setting this to "may" or "encrypt" tells Postfix to encrypt emails using TLS.
- smtpd_tls_auth_only: When set to "yes", plain text authentication will not occur until TLS session has been established. When set to "no", plain text authentication will occur even if the TLS session has not been estabslihed.
- smtpd_tls_key_file: This is the location of the private key file
- smtpd_tls_cert_file: This is the location of the public certificate file
- smtpd_tls_loglevel: Setting this to "1" tells Postfix to log TLS events
- smtpd_tls_session_cache_timeout: It takes some time for the client and server to exchange keys. However, we do not want the client and server to keep a session open indefinately, so we set a timeout of 3,600 seconds.
- smtpd_tls_session_cache_database: TBD
- tls_random_source: TBD
- tls_random_exchange_name: TBD
- Further details are at http://www.postfix.org/TLS_README.html
In the /etc/postfix/master.cf file, remove the comment from the following line to allow outbound on SMTPS port 587.
- smtp = incoming
- smtpd = outgoing
submission inet n - n - - smtpd
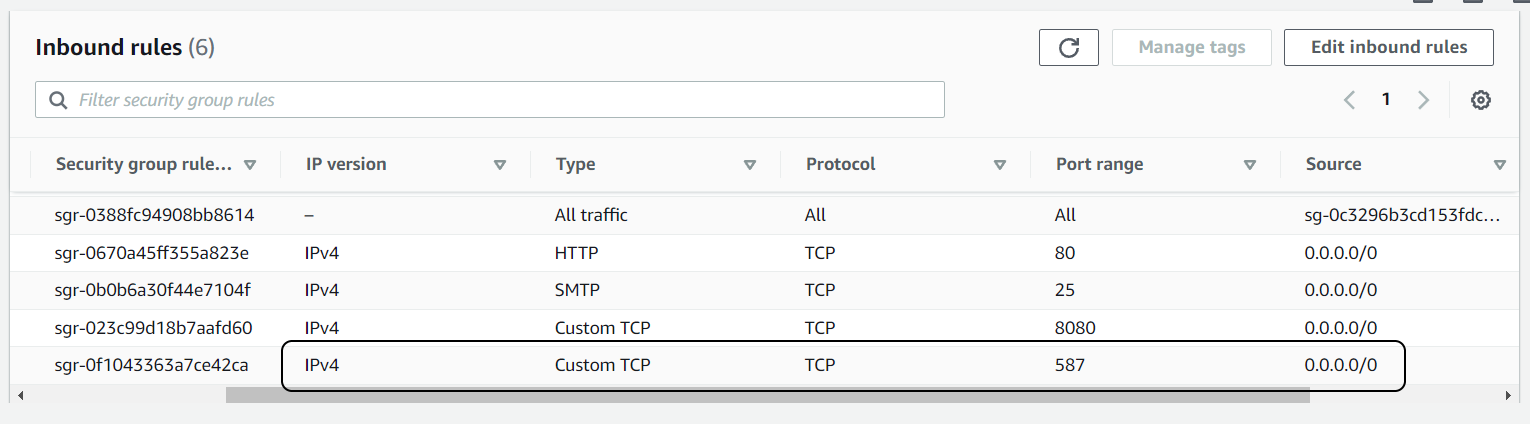
If running an EC2 instance on AWS, ensure the Security Group allows incoming on port 587.
The ps command can be used to determine if your system is using init or systemd. If PID 1 is init, then you will use the service command. If PID 1 is systemd, then you will use the systemctl command.
If your system is using systemd, use the systemctl command to restart postfix.
systemctl restart postfix
If your system is using init, use the chkconfig and service commands to restart postfix.
service postfix restart
If the systemctl status postfix command returns something like this, Postfix is up and running.
~]# systemctl status postfix
● postfix.service - Postfix Mail Transport Agent
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/postfix.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2022-09-05 07:29:46 CDT; 36s ago
Sep 05 07:29:45 mail1 systemd[1]: Starting Postfix Mail Transport Agent...
Sep 05 07:29:46 mail1 postfix/master[23398]: daemon started -- version 2.10.1, configuration /etc/postfix
Sep 05 07:29:46 mail1 systemd[1]: Started Postfix Mail Transport Agent.
Let's use the certutil command with the -L (list) an -d (directory) options to list the certificates in your nssdb (Network Security Services Database). In this example, the nssdb is empty (contains no certificates).
~]# certutil -L -d /etc/pki/nssdb
Certificate Nickname Trust Attributes
SSL,S/MIME,JAR/XPI
The certutil command with the -A (append), -n (name) -t (type) -d (directory) and -i (file) options can be used to append certificates to the nssdb (Network Security Services Database), using the common name (CN) of the certificate (mail.example.com).
certutil -A -n "mail.example.com" -t "TC,," -d /etc/pki/nssdb -i /usr/local/certificates/mail.example.com.cer
And then use the mailx command to send a email over SMTPS port 587. Notice in this example that the SMTP server is "mail.example.com" which is an exact match of the certificate common name (CN). I find that some systems require the certificate common name (CN) to be an exact match of the SMTP server name.
echo test | mailx -s test -S smtp://mail.example.com:587 -S smtp-use-starttls -S ssl-verify=ignore -S nss-config-dir=/etc/pki/nssdb john.doe@example.com
Use Nmap to ensure port 587 is open. Nmap should have the following:
587/tcp open submission
You may also need to Encrypt Dovecot POP3 IMAP traffic using a public/private key pair.
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 