
If you are not familiar with the oc command, refer to OpenShift - Getting Started with the oc command.
A Security Context Constraint is used to control certain things, such as:
- Whether or not a pod can be run as root
- Whether or not a pod can access the host OpenShift system
- Whether or not a pod can access the host OpenShift network
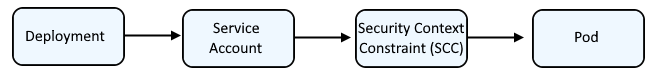
Typically, a Deployment is associated with a Service Account which has a certain Security Context Constraint (SCC) so that the pod runs with a certain Security Context Constraint (SCC).
The oc describe clusterrolebindings command can be used to list the User Accounts and Service Accounts that have a Security Context Constraint.
AVOID TROUBLE
If this command returns something like "Error from server (NotFound)" this probably means there are no User Accounts or Service Accounts associated with the Security Context Constraint.
~]$ oc describe clusterrolebindings system:openshift:scc:restricted
Name: system:openshift:scc:restricted
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Role:
Kind: ClusterRole
Name: system:openshift:scc:restricted
Subjects:
Kind Name Namespace
---- ---- ---------
User john.doe
Group my-group
ServiceAccount my-service-account foo
The oc adm policy remove-scc-from-user command can be used to remove a Security Context Constraints from a User Account.
~]$ oc adm policy remove-scc-from-user restricted john.doe
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:openshift:scc:restricted removed: "john.doe"
Or from a Group.
~]$ oc adm policy remove-scc-from-group restricted -z my-group
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:openshift:scc:restricted removed: "my-group"
Or from a Service Account.
~]$ oc adm policy remove-scc-from-user restricted -z my-service-account
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:openshift:scc:restricted removed: "my-service-account"
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 