OpenShift - List Ingress Route using the oc get ingress command


by
Jeremy Canfield |
Updated: November 17 2022
| OpenShift articles
If you are not familiar with the oc command, refer to OpenShift - Getting Started with the oc command.
- Using an OpenShift route (this is the most common)
- Using an ingress route
- Using a load balancer service
- Assign an external IP address to a service
An OpenShift route or an Ingress route will provide a URL such as http://my-route-my-project.apps.openshift.example.com:8080 which is used to route a request onto a service, which is then routed onto a pod, and then to the container in the pod, and finally to the application running in the container.
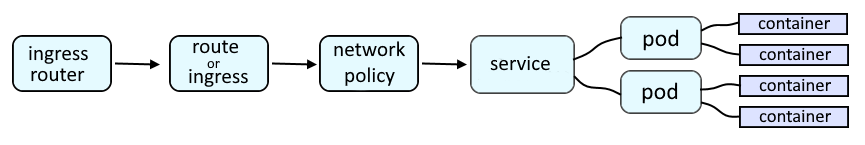
Like this.

The oc get ingress command can then be used the list the Ingress routes in the project/namespace.
~]$ oc get ingress
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
my-ingress-route <none> openshift.example.com 80 4s
The oc describe ingress command can be used to show more details about the ingress route.
~]$ oc describe ingress my-ingress-route
Name: my-ingress-route
Namespace: my-project
Address:
Default backend: default-http-backend:80 (<error: endpoints "default-http-backend" not found>)
Rules:
Host Path Backends
---- ---- --------
openshift.example.com
/my-endpoint my-service:8080 (10.131.4.14:8080)
Annotations: <none>
Events: <none>
Or, the oc get ingress command with the --output json or --output yaml option can be used.
~]$ oc get ingress my-ingress-route --output yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2022-09-13T01:57:37Z"
generation: 1
name: my-ingress-route
namespace: my-project
resourceVersion: "492868937"
uid: 71de4de0-368c-4e72-8a7d-ee202a076727
spec:
rules:
- host: openshift.example.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: my-service
port:
number: 8080
path: /my-endpoint
pathType: Exact
status:
loadBalancer: {}
Did you find this article helpful?
If so, consider buying me a coffee over at 